Early Adopter Nations: Leading the Charge
Several countries have demonstrated significant progress in 5G deployment, showcasing this technology's potential to transform multiple industries. These nations, typically with strong economies and advanced infrastructure, have prioritized 5G investments, resulting in broader service availability and more diverse applications. Their proactive stance has positioned them as innovation leaders, potentially securing long-term economic advantages.
This rapid deployment has sparked a wave of new 5G-enabled applications. The resulting innovation cycle strengthens both infrastructure and services, likely ensuring these countries maintain their leadership position as 5G technology evolves.
Geographic Disparities: Bridging the Gap
While some nations surge ahead, global 5G adoption remains highly uneven. Economic differences and infrastructure gaps create significant barriers for developing regions. Countries with limited resources struggle to deploy and maintain 5G networks, potentially slowing their economic and technological progress.
Closing this digital divide requires international cooperation. Partnerships and targeted assistance could help less developed areas overcome obstacles and access 5G's transformative benefits.
Regulatory Frameworks and Policy Decisions: Shaping the Landscape
Each nation's regulatory approach significantly impacts 5G success. Effective policies covering spectrum allocation, licensing, and cybersecurity create stable environments for deployment. Regional regulatory alignment can facilitate cross-border collaboration and innovation.
Governments must craft policies that balance infrastructure investment with security and consumer protection. This careful equilibrium proves crucial for 5G's long-term success and societal impact.
Economic Implications of 5G Adoption: Driving Growth
5G adoption promises substantial economic benefits across sectors. From improved business connectivity to innovative applications, it may spur growth and create jobs. Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation could see major efficiency gains.
The technology's impact extends beyond economics. Enhanced healthcare access, education, and communication could significantly improve quality of life. Realizing these benefits requires strategic infrastructure development and workforce training.
Technological Advancements: Future-Proofing 5G
Ongoing innovation remains critical for 5G's potential. Improvements in network efficiency, device capabilities, and applications will maximize its transformative power. Continued research in AI and IoT will expand 5G's reach and impact.
As technology progresses, new applications will emerge, creating fresh opportunities. Staying ahead through continuous innovation proves essential for realizing 5G's full potential.
Key Drivers and Inhibitors of 5G Expansion
Key Drivers of 5G Adoption
The growing need for high-speed, low-latency connections drives 5G adoption. Data-heavy applications like AR, VR, and HD streaming fuel this demand. Both consumers and businesses seek faster, more reliable connectivity for their expanding data needs.
Additionally, the IoT's rapid growth creates demand for networks that can support billions of connected devices. 5G's enhanced capacity meets this need better than previous cellular technologies.
Technological Advancements
Breakthroughs in RF technology, antenna design, and signal processing enable 5G development. These allow higher speeds, lower latency, and better spectrum use. Such progress has overcome previous limitations, paving the way for comprehensive connectivity.
New modulation techniques and efficient spectrum use significantly boost 5G performance, enabling faster data transmission than earlier networks.
Economic Incentives
5G's growth potential motivates adoption. Sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and transport could achieve major efficiency gains through 5G technologies. This economic promise encourages both private and public investment.
Government support through financial incentives and policy frameworks has accelerated global 5G rollout.
Regulatory Environment
Effective regulations covering spectrum allocation, interoperability, and security foster 5G deployment. A clear regulatory framework builds confidence and attracts infrastructure investment.
Market Demand
Growing mobile data needs drive 5G rollout. As consumers increasingly rely on mobile devices, demand surges for faster, more reliable services.
Inhibitors of 5G Adoption
High deployment costs hinder adoption in some regions. The substantial infrastructure investment required presents challenges, particularly for smaller providers and developing nations.
Security and privacy concerns also slow adoption. Addressing these through strong protocols and policies remains crucial for building public trust.
Challenges in 5G Implementation: Spectrum Allocation and Interoperability
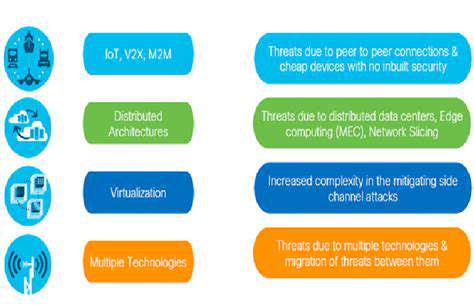
Spectrum Management
5G spectrum management presents major challenges. Different frequencies have unique propagation characteristics. Allocating adequate spectrum for diverse 5G services proves essential for optimal performance. Balancing existing wireless needs with 5G requirements demands international coordination.
Dynamic spectrum usage requires flexible management approaches. Technologies and policies must enable real-time resource allocation based on demand.
Infrastructure Deployment
5G infrastructure rollout faces significant obstacles. The network's scale and complexity demand substantial investment, particularly in urban and rural areas. Integration with existing networks adds further complexity.
High deployment costs in remote areas necessitate innovative funding models and public-private partnerships.
Network Slicing
Implementing network slicing requires advanced virtualization capabilities. Maintaining isolation and security across virtual networks while ensuring performance remains challenging.
Latency and Reliability
Achieving promised latency and reliability levels proves difficult. Developing solutions to minimize interference and congestion remains crucial for 5G success.
Interoperability
Ensuring compatibility across different 5G systems presents challenges. Maintaining standards becomes increasingly complex as technology advances rapidly. Inadequate interoperability could limit 5G's benefits.
Security Concerns
5G networks face numerous cyber threats. Protecting sensitive data transmitted over 5G networks must remain a top priority. Continuous security updates are essential against evolving threats.
User Experience and Adoption
Driving widespread 5G adoption requires demonstrating its benefits. Addressing user concerns about privacy and security proves critical for acceptance. Developing 5G-optimized applications will help attract users.