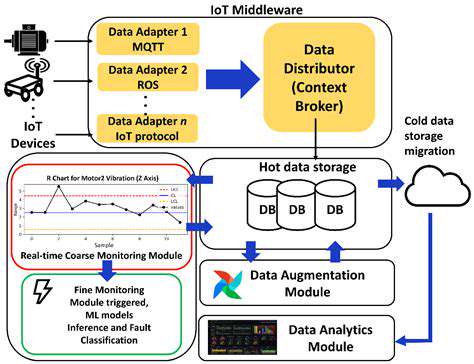
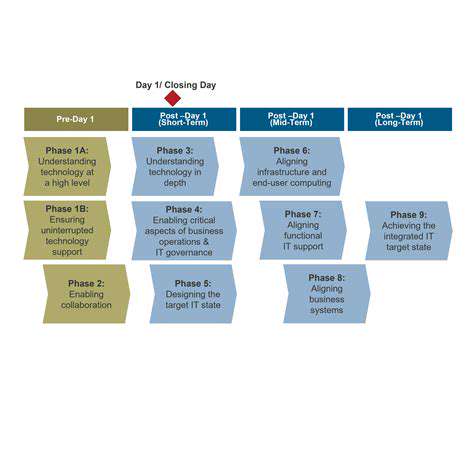
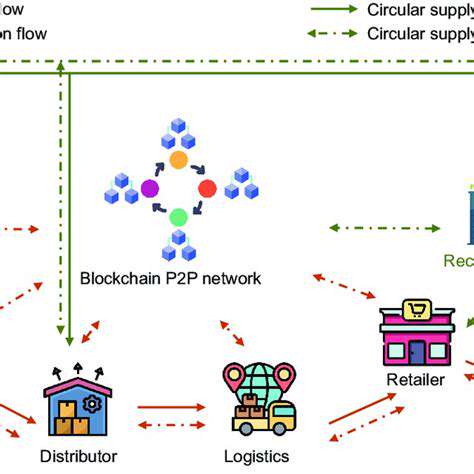
Introduction to AI-Powered Collaborative Problem-Solving

Understanding the Core Concept
AI-powered collaboration fundamentally reshapes team dynamics by introducing intelligent systems that optimize collective efforts. Rather than merely automating repetitive tasks, these tools actively interpret context, predict workflow needs, and provide real-time support to enhance group productivity. The implications extend beyond efficiency—this technology cultivates environments where innovation thrives through seamless coordination.
What sets these systems apart is their capacity to learn from interactions and adapt support mechanisms accordingly. By analyzing communication patterns and work habits, they deliver context-aware assistance that feels intuitive rather than intrusive. This evolutionary approach to teamwork promises to redefine how organizations tackle complex challenges.
Key Features and Benefits
Modern collaboration platforms harness AI's analytical power to process workflow data with remarkable precision. They detect subtle inefficiencies—like recurring meeting delays or document version conflicts—that human teams might overlook. Perhaps most transformative is their multilingual capacity, which dissolves language barriers by providing real-time translation during video conferences and written exchanges.
These systems also excel at talent optimization. By assessing individual contribution patterns, they can suggest ideal role assignments for specific projects. The true value emerges when these tools anticipate needs before users articulate them—recommending relevant files before meetings or flagging potential scheduling conflicts.
Technological Foundations
Recent breakthroughs in neural networks enable these platforms to comprehend nuanced human communication. Unlike earlier systems that relied on keyword matching, current iterations interpret tone, intent, and even unstated implications in team discussions. This depth of understanding allows for remarkably accurate predictions about project roadblocks and resource requirements.
Implementation Challenges
Adoption hurdles persist despite the technology's promise. Security-conscious industries face particular difficulties implementing these solutions while maintaining strict data governance. Organizations must strike a delicate balance—harnessing AI's predictive capabilities without creating surveillance-like environments that stifle creativity.
The human factor remains equally crucial. Teams require training to interact effectively with AI assistants, learning when to trust automated suggestions and when to apply human judgment. Successful implementations typically feature phased rollouts with continuous feedback mechanisms to refine system behavior.
Future Trajectory
Emerging applications suggest these tools will soon customize themselves to industry-specific workflows. Healthcare teams might see AI that understands medical terminology and protocol hierarchies, while engineering groups could receive systems pre-trained on technical documentation standards.
The most exciting developments may come from cross-industry pollination. Collaboration patterns observed in creative agencies could inspire new approaches for scientific research teams, with AI serving as the connective tissue between disparate domains. This cross-pollination potential makes the technology's future particularly compelling.
Enhancing Communication and Knowledge Sharing
Leveraging AI for Enhanced Collaboration
Contemporary teams increasingly rely on intelligent systems to optimize their communication rhythms. These platforms do more than facilitate conversations—they analyze discussion patterns to identify unspoken consensus or brewing conflicts. By mapping communication networks, they reveal how information actually flows within organizations, which often differs dramatically from formal reporting structures.
The matching algorithms represent another leap forward. Rather than simply connecting colleagues by department or seniority, these systems identify complementary problem-solving styles—pairing big-picture thinkers with detail-oriented executors when tackling complex initiatives. This nuanced approach to team formation consistently yields higher-quality outcomes than traditional grouping methods.
AI-Powered Knowledge Management Systems
Modern knowledge platforms have evolved from static repositories to dynamic learning ecosystems. They now track which solutions get reused and refined, creating organic quality filters. When an engineer in Berlin searches for troubleshooting methods, the system might prioritize approaches that Mumbai colleagues have successfully adapted multiple times.
The most advanced systems employ semantic search that understands queries contextually. A search for client onboarding will return different materials to HR professionals versus sales teams, based on each department's historical usage patterns and project requirements.
Personalized Learning and Skill Development
Adaptive learning platforms now tailor content delivery based on multiple factors—not just quiz scores, but also time-of-day engagement patterns and preferred media formats. Some systems even adjust material difficulty based on physical indicators like typing speed during exercises, providing real-time challenge calibration.
Forward-thinking organizations use these tools to create skill maps that visualize how individual capabilities interlock across teams. This approach helps identify critical knowledge gaps before they cause project delays, allowing for proactive upskilling rather than reactive damage control.
Automated Communication and Task Management
Intelligent scheduling represents just the beginning. Contemporary systems analyze meeting outcomes to suggest optimal durations—recognizing that brainstorming sessions require different time allocations than status updates. They can even propose agenda items based on pending action items from previous discussions.
The most sophisticated task managers now incorporate progress pulse features that detect early warning signs like slowing comment frequency or increasing document revision cycles. These subtle indicators often surface potential roadblocks weeks before traditional metrics would raise alerts, enabling preemptive course correction.