The Future of Combating Antibiotic Resistance
The Rise of Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) represents one of modern medicine's most pressing challenges, undermining our ability to treat common infections. Reckless antibiotic use in both healthcare and agriculture has accelerated this dangerous phenomenon, allowing resistant bacterial strains to flourish. These superbugs can withstand multiple drug treatments, leaving physicians with dwindling options for patients.
The ripple effects extend throughout healthcare systems, driving up costs while compromising patient care. Vulnerable groups including children, seniors, and those with weakened immune systems face particularly severe consequences from these treatment-resistant infections. Without immediate, coordinated action, we risk returning to a pre-antibiotic era where minor infections could prove fatal.
Innovative Strategies for New Antimicrobials
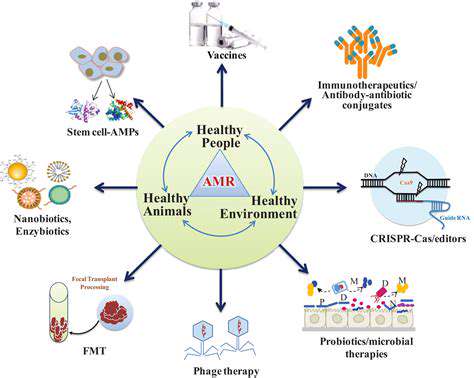
Researchers are exploring creative solutions to outsmart resistant bacteria. One approach involves investigating existing medications for unexpected antibacterial properties, potentially accelerating treatment development. Simultaneously, scientists are designing drugs that attack bacteria through novel mechanisms - disrupting their protective layers, sabotaging essential biological processes, or blocking protein production.
These cutting-edge approaches could bypass existing resistance mechanisms and provide much-needed therapeutic alternatives. Genetic research is also uncovering bacterial weaknesses that could lead to highly targeted treatments. Beyond drug development, improved delivery methods aim to maximize effectiveness while minimizing side effects for patients.
Combating Antibiotic Resistance: A Multifaceted Approach
Addressing AMR requires coordination across multiple fronts. Educating both medical professionals and the public about responsible antibiotic use forms the foundation of any effective strategy. This includes resisting pressure to prescribe antibiotics for viral illnesses where they prove ineffective.
Agricultural practices must also evolve, with stricter controls on antibiotic use in livestock to prevent resistant strains from entering the food chain. Policy makers play a crucial role in establishing and enforcing these safeguards.
Sustained investment in antimicrobial research remains critical, requiring collaboration between academic institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory agencies. Comprehensive surveillance systems will help track resistance patterns, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment protocols and containment strategies.