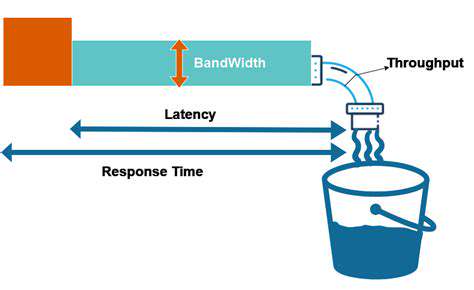
While chopping might seem basic, mastering this skill truly distinguishes casual cooks from culinary experts. Precision in knife work hinges on three critical factors: your grip on the handle, the consistent angle of the blade, and the rhythmic motion of your cuts. Over a decade of professional cooking has shown me that ingraining these fundamentals into muscle memory not only prevents injuries but dramatically improves efficiency in meal preparation.
Interactive Learning Experiences: Engaging Students and Enhancing Motivation

Interactive Simulations for Enhanced Understanding
Modern education increasingly relies on interactive simulations to make abstract concepts tangible. These dynamic tools let learners manipulate parameters, witness consequences, and gain intuitive grasps of scientific laws, historical patterns, or mathematical relationships. Unlike passive reading, this hands-on approach creates neural pathways that significantly boost information retention - particularly valuable for visualizing phenomena that static diagrams struggle to convey.
Their applications span diverse fields: chemistry students can safely explore molecular interactions without lab hazards, while history classes use interactive timelines to analyze cause-and-effect relationships in geopolitical events. This versatility makes simulations indispensable across educational settings.
Gamified Learning Platforms for Motivation and Engagement
Educational technology now incorporates game design principles to transform study sessions into captivating experiences. Reward systems featuring points, achievement badges, and friendly competition tap into natural motivational psychology. This blend of entertainment and education proves particularly effective for students who disengage from conventional teaching methods.
Sophisticated platforms adapt to individual progress, offering customized learning journeys with real-time feedback. Many also facilitate peer collaboration, creating communities where knowledge sharing becomes part of the engaging experience.
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality for Immersive Learning
Cutting-edge VR technology transports learners to meticulously reconstructed historical sites or complex biological systems, while AR overlays enrich real-world environments with educational annotations. This sensory immersion leads to deeper cognitive processing, making lessons about ancient civilizations or molecular structures feel vividly real rather than abstract concepts.
Medical students might practice virtual surgeries, while architecture classes could explore scaled-down building models from all angles. These technologies dissolve physical classroom limitations, offering experiential learning that textbooks simply cannot match.
Future Trends and Implications: Shaping the Educational Landscape
Personalized Learning Experiences
Advanced algorithms now enable educational platforms to continuously adapt to each learner's demonstrated competencies. By analyzing response patterns, these systems identify knowledge gaps and automatically adjust content delivery - not just varying difficulty, but tailoring presentation styles to match individual cognitive preferences. A visually-oriented student might receive animated explanations, while an auditory learner gets podcast-style content.
This personalization extends to pacing, with mathematics programs that detect when to introduce more challenging problems or revert to foundational concepts. Such adaptive learning represents a seismic shift from one-size-fits-all education to truly customized knowledge acquisition.
Enhanced Accessibility and Inclusivity
Artificial intelligence is demolishing educational barriers for neurodiverse learners and students with physical challenges. Real-time transcription services, adaptive interfaces for motor impairments, and dyslexia-friendly formatting options create equitable learning environments. These innovations ensure educational content conforms to students' needs rather than forcing students to conform to rigid systems.
Multilingual AI tutors can simultaneously translate lectures while culturally adapting examples, making education globally accessible. For visually impaired learners, advanced haptic feedback systems translate graphical information into tactile experiences. Such technologies don't just accommodate differences - they celebrate cognitive diversity as an asset to collaborative learning.
The cumulative impact of these advancements points toward an educational paradigm where personalized pathways, immersive technologies, and universal accessibility converge to make quality learning experiences available to all. Rather than replacing educators, these tools empower teachers to focus on mentorship and critical thinking development while technology handles individualization and access.