Blockchain Technology: Transforming Supply Chains
Modern supply chains are undergoing a radical transformation thanks to blockchain technology. By offering a transparent and secure platform, blockchain enables businesses to track goods and materials at every stage of the process. This unprecedented level of visibility ensures accountability while minimizing risks like fraud and counterfeiting. Each transaction gets recorded on a shared, unchangeable ledger, creating a complete history of a product's journey from origin to consumer. The result? A supply chain that's both more trustworthy and efficient.
One of blockchain's most powerful features is the permanence of its records. Once data enters the ledger, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or erase. This characteristic builds confidence among all participants while removing the necessity for middlemen. The elimination of these intermediaries cuts verification and reconciliation costs, making the entire process smoother for everyone involved.
Decentralization and Enhanced Security
The distributed nature of blockchain sets it apart from traditional systems. Instead of a single controlling entity, the network shares power and responsibility across all participants. This decentralized approach creates formidable barriers against data tampering and network disruptions. By spreading control, blockchain establishes a foundation of transparency where every participant can verify transactions independently.
Security gets further reinforced through advanced cryptography. Every transaction receives cryptographic protection, making forgery or alteration practically impossible. This built-in security represents a significant upgrade over conventional systems that rely on centralized authorities - a design that often creates exploitable weaknesses.
Improved Efficiency and Transparency
Blockchain introduces remarkable efficiency gains by automating and digitizing supply chain transactions. This shift away from manual processes reduces human error while speeding up operations. Perhaps most importantly, blockchain's transparency creates an environment where accountability becomes the norm. Stakeholders gain real-time visibility into product movements, allowing quicker responses to potential issues and reducing costly delays.
The shared, immutable ledger fosters unprecedented transparency across the supply chain network. When all parties access the same verified information, trust increases while uncertainty decreases. This clarity promotes better collaboration and enables faster resolution of any problems that might emerge during operations.
Future Implications and Applications
Blockchain's potential extends far beyond basic tracking functions. The technology promises to create supply chains that are not only more efficient but also more resilient in the face of disruptions. Future applications include automated contract execution, simplified payment processing, and advanced risk management solutions that can adapt to changing conditions.
As blockchain continues to evolve, we can anticipate even more sophisticated capabilities emerging. Developers are working on more intuitive interfaces to encourage wider adoption while exploring novel use cases across industries. These advancements will likely drive further improvements in global supply chain security and efficiency.
Key Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chain Visibility
Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology revolutionizes supply chain visibility by maintaining an unalterable record of every product movement and transaction. This comprehensive history lets businesses track items from their source to final delivery, creating extraordinary transparency. Companies can locate their products with precision at any moment, maintaining control and ensuring accountability throughout the journey. The meticulous documentation significantly deters counterfeiters and fraudsters, as every action leaves a verifiable trail.
This enhanced traceability also enables rapid response to quality issues. When problems arise, the detailed blockchain record helps quickly identify their source, allowing for immediate corrective measures. Such capabilities prove invaluable for maintaining product quality and consumer confidence. For businesses committed to ethical sourcing, blockchain provides concrete proof of compliance with environmental and social standards at every supply chain stage.
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Blockchain delivers substantial efficiency improvements by automating traditionally manual processes. Documentation bottlenecks, verification delays, and information mismatches become rare occurrences, speeding up goods movement and shortening lead times. These operational improvements translate directly to cost savings as businesses eliminate redundant steps and optimize resource use.
The automation of paperwork and communications through blockchain slashes administrative expenses. By enabling direct interactions between supply chain partners, the technology removes unnecessary intermediaries, creating a leaner, more profitable system for all involved. The reduction in manual processes also means fewer errors and greater overall accuracy - crucial factors in maintaining an efficient supply chain.
Increased Security and Reduced Risk
Blockchain's decentralized architecture and encryption protocols provide exceptional security for supply chain data. The permanent nature of ledger entries makes unauthorized alterations virtually impossible, dramatically lowering fraud and data breach risks. These security features build trust among participants, encouraging collaboration based on confidence in the system's integrity.
The distributed ledger design adds another layer of protection. With multiple copies of the ledger existing across the network, the failure of any single node doesn't jeopardize the entire system. This redundancy protects against data loss while ensuring continuous access to critical supply chain information. The transparency enabled by blockchain also helps businesses identify and mitigate potential risks before they escalate.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
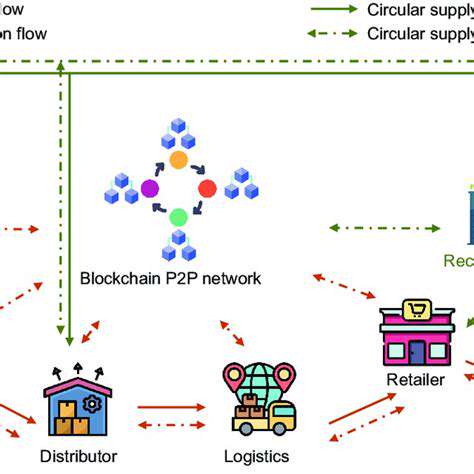
Blockchain promotes unprecedented collaboration among supply chain participants, from manufacturers to end retailers. The shared ledger serves as a single, authoritative information source, eliminating discrepancies and fostering cooperative relationships. This common platform allows real-time data sharing, with all participants able to view and update information simultaneously.
Improved communication channels benefit the exchange of crucial operational details like order status, shipping updates, and quality reports. Immediate information sharing reduces delays and misunderstandings, creating a more responsive supply chain network. These communication improvements also enable faster adaptation to market changes or unexpected supply chain disruptions.
Flavor profiles reveal the distinctive qualities of culinary creations, blending taste, aroma, and texture in unique combinations. These characteristics emerge from the interplay of acids, sugars, fats, and seasonings. Understanding these profiles unlocks the art of perfect pairings. For instance, a rich, umami-dominant dish achieves balance when paired with bright, acidic elements that provide a refreshing contrast.

Future Trends and Opportunities in Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chains
Emerging Technologies and Applications
The future landscape across industries will experience profound changes as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT technologies advance. These innovations are generating novel applications with transformative potential. AI integration into existing systems is producing more intelligent, streamlined operations. Manufacturing provides a clear example, where AI-driven robotics optimize production while minimizing errors.
Meanwhile, the expanding IoT ecosystem enables unprecedented real-time data collection and analysis. These capabilities yield valuable insights into consumer behavior and market dynamics - information critical for strategic decision-making. Adapting to these technological shifts will become essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Concerns
Environmental awareness is reshaping business priorities, driving widespread adoption of sustainable practices. Companies increasingly focus on reducing environmental impact through renewable energy investments, resource optimization, and circular economy models. Sustainability has evolved from a niche consideration to a fundamental business requirement in today's market.
Consumer demand for eco-friendly products continues to grow as buyers increasingly favor brands demonstrating environmental responsibility. This shift creates significant opportunities for companies prioritizing sustainable operations. Regulatory frameworks and government incentives will likely play a growing role in promoting environmentally conscious business practices.
Globalization and Emerging Markets
The global economic landscape continues evolving as emerging markets gain prominence. These developing economies present both challenges and opportunities for businesses seeking expansion. Success in these markets requires deep understanding of local customs, regulations, and cultural contexts.
Advancements in international trade agreements and infrastructure will further facilitate cross-border commerce and investment. Businesses must adapt their strategies to meet the specific needs of consumers in these growing markets. Companies that successfully navigate these complexities position themselves for substantial growth opportunities.
Innovation and Creative Problem Solving
Future success will increasingly depend on innovative thinking and creative solutions to complex challenges. Organizations demonstrating agility in adapting to market changes and identifying emerging opportunities will lead their industries. Cultivating environments that encourage experimentation and continuous learning becomes crucial for maintaining this competitive edge.
Adopting new technologies and unconventional approaches, combined with willingness to challenge conventional wisdom, will define industry leaders. This requires commitment to research and development, along with organization-wide emphasis on innovation. Continuous adaptation and learning remain fundamental to meeting evolving consumer expectations.