Introduction to Edge Computing
Key Concepts in Edge Computing
Edge computing fundamentally shifts data processing from distant clouds to local sources. This paradigm change cuts latency dramatically, enabling instant responses for time-sensitive applications. Rather than flooding networks with raw data, smart edge devices analyze information locally, forwarding only crucial insights to central systems. This approach eases network strain while boosting efficiency, particularly in areas with spotty connectivity.
To fully appreciate edge computing's value, one must understand its core elements. The ecosystem comprises intelligent sensors, local processing units, and distributed servers - all collaborating to handle data where it's created. These components often feature specialized architectures tailored for specific tasks, maximizing performance in real-world conditions. Advanced communication protocols serve as the glue connecting these distributed systems, ensuring smooth data flow across the network.
Applications of Edge Computing in Diverse Fields
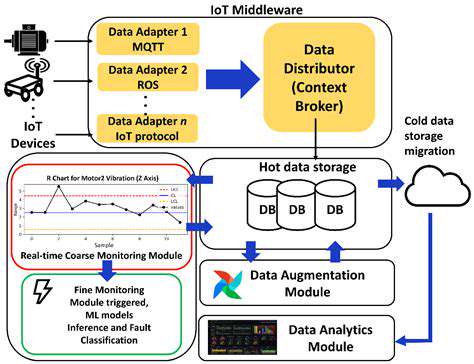
The industrial sector has embraced edge computing for equipment monitoring and maintenance. Modern factories deploy smart sensors that detect mechanical issues before they cause failures, enabling preemptive repairs that minimize production halts. For instance, vibration analysis at the machine level can predict bearing wear, triggering maintenance requests before catastrophic breakdowns occur.
Transportation systems reap substantial benefits from edge processing. Autonomous vehicles depend on split-second decisions from sensor data - a requirement cloud computing can't reliably meet. By processing lidar, radar and camera inputs locally, self-driving cars maintain the rapid response times essential for safe navigation. This local processing capability proves particularly valuable in areas with poor cellular coverage.
The healthcare sector utilizes edge computing for real-time patient monitoring, while retailers employ it for personalized shopping experiences. Across industries, the common thread is the need for immediate data processing without cloud dependency.
Remote operations benefit tremendously from edge computing's offline capabilities. Oil rigs, mining operations and agricultural sites can maintain critical systems even when internet access is intermittent or nonexistent.
Security improves significantly with edge computing's distributed architecture. Sensitive data remains closer to its source, reducing exposure during transmission. Financial institutions and healthcare providers particularly value this enhanced protection.
The decentralized nature of edge systems also provides operational flexibility. Companies can scale processing power precisely where needed without overhauling entire networks.
Real-Time Industrial Automation and Control
Real-time Control in Manufacturing
Modern factories increasingly rely on edge-powered automation for precision manufacturing. Local processing units analyze sensor data from robotic arms and conveyor systems, making micro-adjustments in milliseconds. This instantaneous control maintains tight tolerances in pharmaceutical production, semiconductor fabrication, and automotive assembly lines where quality demands perfection.
Predictive Maintenance and Proactive Actions
Vibration analysis and thermal imaging at the edge detect equipment anomalies long before human operators would notice. Advanced algorithms compare current readings against historical patterns, scheduling maintenance during planned downtime rather than after catastrophic failures. This proactive approach has reduced unplanned outages by up to 45% in some manufacturing plants.
Enhanced Safety and Security
Edge devices continuously monitor environmental conditions like gas concentrations or structural stresses. When thresholds are exceeded, they can initiate shutdown procedures before human operators even receive alerts. This rapid response capability has proven particularly valuable in chemical plants and nuclear facilities where seconds matter.
Optimized Energy Consumption
Smart factories use edge computing to match energy usage with production demands. Lighting, HVAC and machinery power adjust dynamically based on real-time occupancy and production schedules. Some automotive plants have achieved 30% energy reductions through such edge-controlled optimizations.
Improved Quality Control and Product Consistency
Vision systems powered by edge AI inspect every product on the line at speeds impossible for human workers. Microscopic defects in electronics or packaging get flagged immediately, allowing instant adjustments to manufacturing parameters. This constant quality monitoring has reduced waste by up to 60% in some consumer goods factories.
Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization
Edge devices track shipments from warehouse to destination, monitoring location, temperature and handling conditions. This granular visibility allows logistics teams to reroute shipments around delays or adjust storage conditions remotely. The pharmaceutical industry particularly benefits from this real-time monitoring of sensitive medical shipments.
Enhanced Video Surveillance and Security

Enhanced Video Surveillance and Security System Integration
Modern security systems combine high-resolution cameras with intelligent analytics at the edge. This integration enables proactive threat detection rather than passive recording, transforming security from reactive to preventive. Airports and financial institutions now deploy systems that can identify unattended bags or suspicious loitering in real-time.
Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning
Edge-based AI models recognize weapons, aggressive gestures, or perimeter breaches without cloud dependency. These systems continuously learn from new data, improving detection accuracy over time while respecting privacy through local processing.
Improved Data Storage and Management
Modern systems use intelligent compression to preserve crucial footage while discarding uneventful periods. Some banks now retain ATM footage for 180 days while reducing storage needs by 70% through smart edge processing.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting Capabilities
When edge systems detect unauthorized access attempts, they can trigger alarms, lock doors, and alert security teams simultaneously. This coordinated response has reduced response times from minutes to seconds in retail loss prevention scenarios.
Remote Access and Mobile Integration
Security directors now monitor multiple sites from mobile devices, receiving push notifications for critical events. This mobility has revolutionized security operations, enabling faster decision-making during emerging situations.