Challenges and Future Directions
Improving Discharge Planning Accuracy
Accurate and timely discharge planning is crucial for patient safety and optimal post-hospitalization outcomes. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data, including medical history, diagnoses, medications, and predicted needs, to identify potential complications and tailor discharge plans accordingly. This improved accuracy can lead to fewer readmissions and better patient management in the community setting. By proactively identifying high-risk patients, AI can facilitate the development of personalized discharge plans, ensuring patients receive the necessary resources and support to succeed at home.
Furthermore, AI can help to flag potential issues that might otherwise be missed, such as medication interactions or unmet social needs. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of adverse events and improve the overall quality of care provided during the transition from hospital to home.
Streamlining the Discharge Process
The current discharge process often involves multiple stakeholders, paperwork, and communication challenges, leading to delays and inefficiencies. AI-powered systems can automate many of these tasks, such as generating discharge summaries, scheduling follow-up appointments, and coordinating care with community healthcare providers. This automation can significantly reduce the administrative burden on healthcare professionals, allowing them to focus on patient care and improve the overall efficiency of the discharge process.
By streamlining communication and data flow, AI can eliminate bottlenecks and reduce the time it takes to discharge patients. This efficiency translates to faster access to post-hospitalization care and support, ultimately improving patient satisfaction and reducing the risk of complications.
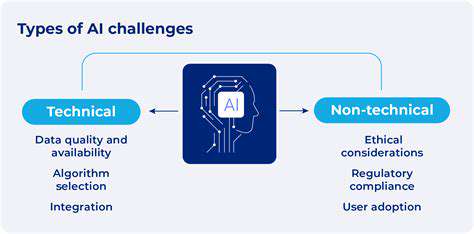
Addressing Data Integration and Standardization
Effective AI implementation for discharge planning relies heavily on the availability of high-quality, standardized patient data. Integrating data from various sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), pharmacy systems, and social services databases, is a significant challenge. Standardization of data formats and interoperability between systems are essential to ensure consistent and reliable input for AI algorithms.
Ensuring Ethical and Responsible AI Deployment
The use of AI in healthcare, including discharge planning, raises ethical concerns regarding data privacy, bias in algorithms, and transparency in decision-making. Robust ethical guidelines and regulations are necessary to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly. These guidelines should address data security, algorithm fairness, and the need for human oversight in the decision-making process. Transparency in how AI algorithms arrive at recommendations is vital to build trust and ensure patient safety.
Furthermore, efforts to mitigate bias in the data used to train AI models are critical. Bias in historical data can lead to discriminatory outcomes in discharge planning, potentially exacerbating existing health disparities. Careful attention to data quality and algorithm validation is essential to avoid these pitfalls.
Developing AI-Driven Personalized Care Plans
AI can play a transformative role in creating personalized discharge plans tailored to the specific needs of each patient. By analyzing individual patient characteristics, preferences, and predicted needs, AI can generate discharge plans that are more effective and efficient in supporting the patient's transition to home. This personalized approach can improve patient adherence to treatment plans, reduce readmission rates, and enhance overall patient satisfaction.
This personalized approach can be extended to include tailored education for patients and caregivers, ensuring that they possess the knowledge and tools required for successful self-management. Such support significantly improves long-term health outcomes.
Evaluating the Impact and Measuring Success
Rigorous evaluation is essential to assess the effectiveness of AI-driven discharge planning interventions. Metrics should include readmission rates, patient satisfaction scores, length of stay in post-acute care facilities, and the cost-effectiveness of the AI system. Tracking these metrics allows for continuous improvement of AI algorithms and processes, ensuring that the system remains relevant and effective in addressing the evolving needs of patients.
The evaluation should also consider the impact on healthcare professionals, assessing changes in their workload, job satisfaction, and ability to focus on direct patient care. A holistic evaluation is necessary to understand the full impact of AI on the entire healthcare system.