Decentralized Power: Edge Computing Explained
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing represents a fundamental shift in data processing philosophy. Instead of sending information to distant cloud servers, processing happens locally—right where the data originates. This approach eliminates the lag time of round-trip data transmission, which is particularly crucial for time-sensitive applications like facial recognition in security systems.
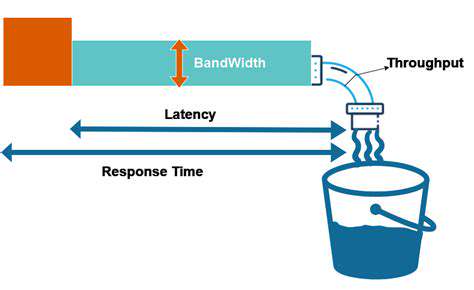
By keeping processing local, edge computing solves two major problems simultaneously: it reduces network congestion while dramatically improving response times. For applications requiring instant analysis—like identifying persons of interest in a crowd—this distributed approach delivers results when centralized systems would still be waiting for data to make the round trip to a server farm hundreds of miles away.
The Role of Edge Computing in Real-Time Facial Recognition
Security systems leveraging facial recognition benefit enormously from edge computing architecture. When cameras can analyze faces locally, they provide immediate feedback without waiting for distant servers. This localized processing enables security personnel to respond to threats in real-time rather than reviewing footage after incidents occur.
The advantages extend beyond speed. Edge-based systems continue functioning even with intermittent internet connectivity, making them ideal for remote locations. This reliability ensures continuous operation when it matters most—during security emergencies where every second counts.
Key Advantages and Challenges of Edge Computing for Facial Recognition
Edge computing offers three transformational benefits for facial recognition: reduced latency, enhanced privacy, and lower bandwidth requirements. Processing data locally means sensitive biometric information doesn't need to traverse potentially vulnerable networks. This localized approach also reduces infrastructure costs by minimizing cloud computing expenses.
However, challenges remain. Securing thousands of edge devices requires robust protocols to prevent tampering. Standardizing performance across diverse hardware presents another hurdle. Perhaps most crucially, edge devices must deliver accuracy comparable to cloud systems despite having less computational power. Solving these challenges will determine how widely edge-based facial recognition gets adopted.
Optimizing Facial Recognition Algorithms on Edge Devices

Improving Accuracy
Creating highly accurate facial recognition for edge devices starts with comprehensive training data. Diverse datasets representing all demographics are non-negotiable for minimizing algorithmic bias. Modern techniques like generative adversarial networks (GANs) can create synthetic training data to fill representation gaps in existing datasets.
Algorithm selection proves equally crucial. Lightweight convolutional neural networks specifically designed for mobile processors can achieve near-cloud-level accuracy without requiring expensive hardware. These optimized models extract only the most relevant facial features, ignoring extraneous data that would slow processing.
Handling Occlusion and Lighting Variations
Real-world conditions demand algorithms that work despite obstacles. Advanced systems now use attention mechanisms to focus on visible facial features when portions are obscured. Similarly, adaptive normalization techniques automatically adjust for varying lighting conditions—from bright sunlight to dim indoor environments.
The best systems employ multi-modal verification, combining facial recognition with other biometrics when conditions aren't ideal. This layered approach maintains security even when primary recognition methods face challenges.
Data Preprocessing and Enhancement
Before analysis begins, smart preprocessing ensures optimal input quality. Automated filters remove noise and artifacts while preserving critical facial features. Dynamic range adjustment compensates for poor lighting, and face alignment algorithms standardize orientation for more reliable matching.
On edge devices with limited resources, these preprocessing steps often use highly optimized algorithms that leverage specialized hardware acceleration. This careful preparation enables the main recognition algorithm to work with clean, standardized input regardless of original capture conditions.
Real-time Performance Optimization
Speed optimization requires meticulous engineering at every level. Quantization reduces model size without significant accuracy loss, while pruning removes unnecessary neural network connections. Hardware-aware design ensures algorithms fully utilize available processors, whether GPUs, NPUs, or specialized AI accelerators.
The most advanced systems implement dynamic complexity scaling—automatically adjusting processing intensity based on device workload and power constraints. This intelligent resource management allows consistent real-time performance across diverse edge devices.
Security Considerations
Edge devices present unique security challenges as potential physical access points. Robust encryption protects stored facial templates, while secure enclaves prevent unauthorized access to live processing. Regular over-the-air updates ensure devices stay protected against emerging threats.
Perhaps most importantly, modern systems incorporate anti-spoofing measures to distinguish real faces from photographs or digital reproductions. These countermeasures use subtle biological signals—like microexpressions and blood flow patterns—that are nearly impossible to fake.
Real-World Applications and Future Trends

Real-World Applications in Various Sectors
Facial recognition technology has moved far beyond security applications. Airports now use it for seamless boarding processes, while retailers analyze customer emotions to optimize store layouts. Healthcare providers employ facial analysis for pain assessment and early symptom detection, demonstrating the technology's life-saving potential.
Smart cities integrate facial recognition with surveillance systems to locate missing persons quickly. Meanwhile, banks use the technology for frictionless authentication, eliminating cumbersome password requirements. Each successful implementation demonstrates how facial recognition can solve real-world problems when deployed thoughtfully.
Future Technological Advancements and Implications
The next generation of facial recognition will likely focus on three areas: improved privacy protections, greater accuracy under challenging conditions, and expanded functionality. Emerging techniques like federated learning may enable model improvement without centralized data collection. At the same time, 3D facial recognition promises better performance with masks or other obstructions.
Perhaps most intriguingly, future systems may analyze microexpressions to assess emotional states or detect deception. Such capabilities could revolutionize fields from customer service to law enforcement—provided appropriate ethical guidelines accompany them.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Impact
As capabilities expand, so do ethical responsibilities. Clear policies must govern data collection, retention, and usage to prevent abuse. Transparency about system limitations helps manage expectations, while opt-out provisions preserve individual autonomy.
The most sustainable implementations will balance security benefits with personal privacy rights. Ongoing public dialogue and responsive regulation will ensure facial recognition develops as a tool for social benefit rather than surveillance overreach. With proper safeguards, this powerful technology can enhance safety and convenience without compromising fundamental freedoms.