Introduction to Intelligent Building Management

Defining Intelligent Buildings
Intelligent buildings leverage technology to optimize various aspects of their operation, from energy management to occupant comfort. This technology integration allows for a more efficient and sustainable building environment, ultimately reducing operational costs and improving the overall experience for occupants. By seamlessly integrating different systems, intelligent buildings can respond dynamically to changing conditions and user needs. This dynamic response is a key differentiator from traditional buildings.
These buildings often incorporate a range of smart technologies, such as sensors, actuators, and control systems, to monitor and adjust building parameters in real-time. This real-time feedback loop is crucial for optimizing performance and achieving sustainability goals.
Key Components of Intelligent Building Systems
Central to intelligent building systems are sophisticated control systems that monitor and manage various aspects of the building. These systems often utilize complex algorithms and data analytics to make informed decisions about energy consumption, lighting, temperature, and security. A key element is the seamless integration of these systems to ensure coordinated operation. This integration allows for effective management of resources and creates a unified platform for building management.
Smart sensors play a vital role in gathering real-time data about the building environment. They provide valuable insights into occupancy patterns, energy usage, and environmental conditions, enabling proactive adjustments and optimized resource allocation. These sensors are essential for the dynamic feedback loop that is characteristic of intelligent buildings.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Intelligent building systems are designed to maximize energy efficiency and promote sustainability. By monitoring energy consumption patterns and adjusting operational parameters accordingly, these systems can significantly reduce energy waste. This reduction in energy consumption translates directly to lower operational costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
Sustainable practices, such as optimizing lighting schedules and controlling HVAC systems based on real-time occupancy, are integral components of intelligent building design. These practices contribute to a more environmentally responsible approach to building operation.
Occupant Comfort and Experience
Intelligent buildings strive to create a comfortable and enjoyable environment for occupants. By adjusting temperature, lighting, and air quality based on occupancy patterns, these buildings personalize the experience for each user, optimizing comfort levels.
Personalized comfort is a key factor in creating a productive and positive work environment. This enhanced comfort leads to increased occupant satisfaction and a more efficient workplace.
Building Automation and Control Systems
Building automation and control systems (BACS) are the backbone of intelligent buildings. These systems are responsible for controlling and coordinating various building functions, including lighting, HVAC, security, and access control. They ensure a smooth and efficient operation of the building.
Advanced building automation systems often feature user-friendly interfaces and remote monitoring capabilities, allowing building managers to effectively control and manage the building from anywhere. This remote access is particularly important for large and complex facilities.
Security and Safety Enhancements
Intelligent building systems often incorporate advanced security features to enhance safety and protect occupants. These features might include access control systems, surveillance cameras, and alarm systems that are integrated and automated to provide real-time security monitoring.
Enhanced security measures contribute to a safer and more secure environment for occupants. The integration of security systems with other building systems allows for a holistic approach to building safety and security.
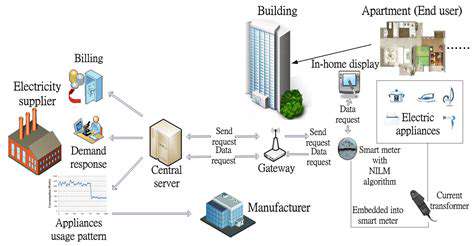
Enhancing Occupant Comfort and Well-being
Improving Thermal Comfort
Maintaining a comfortable temperature throughout a building is crucial for occupant well-being. Proper insulation and air sealing strategies can significantly reduce energy consumption while simultaneously enhancing thermal comfort. This leads to a more pleasant and productive environment, positively impacting occupant satisfaction and reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. Implementing efficient HVAC systems, coupled with smart thermostats, allows for personalized temperature control and further minimizes energy waste.
Effective thermal comfort measures also extend to the use of appropriate window treatments and shading devices. These simple solutions can significantly reduce solar heat gain, especially in hot climates. Properly designed and positioned windows, as well as strategically placed vegetation, can further enhance the natural cooling of a space, resulting in a more sustainable and comfortable indoor environment. Careful consideration of these factors can lead to substantial reductions in energy consumption and increased occupant satisfaction.
Optimizing Acoustic Conditions
Noise pollution can significantly impact occupant comfort and well-being. Reducing noise levels through effective soundproofing strategies is essential for creating a peaceful and productive environment. This involves careful selection of building materials with good sound absorption properties, such as acoustic panels or carpeting, to minimize reverberation and echo. Implementing sound barriers, such as double-glazed windows, can also significantly reduce external noise intrusion.
In addition to passive strategies, active noise control systems can be employed to further mitigate noise levels. These systems use specialized technologies to generate counteracting sound waves, effectively canceling out unwanted noise. This approach can be particularly beneficial in high-traffic areas or spaces with persistent background noise. Implementing these acoustic solutions can contribute to a more calm and focused atmosphere, fostering better concentration and overall comfort.
Enhancing Visual Environments
Natural light is essential for creating a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. Maximizing natural light through strategically positioned windows and skylights can significantly reduce the need for artificial lighting, resulting in lower energy costs and a more pleasant visual experience. Properly designed daylighting strategies can also improve the mood and well-being of occupants, reducing feelings of stress and fatigue.
Careful consideration of the visual aspects of a space, including the use of color, lighting, and artwork, can greatly affect occupant comfort. Thoughtfully selected colors and lighting schemes can create a calming or invigorating atmosphere. The incorporation of art and natural elements, like plants, can further enhance the visual appeal and overall well-being of the occupants. A well-designed visual environment contributes significantly to the overall comfort and productivity of the space.
Promoting Air Quality
Maintaining good indoor air quality (IAQ) is paramount for occupant comfort and health. Implementing effective ventilation systems that ensure adequate fresh air exchange is essential. This includes strategies like using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to remove pollutants and allergens from the air. Maintaining proper humidity levels is also crucial for minimizing the growth of mold and mildew, which can significantly impact IAQ and occupant comfort.
Addressing potential sources of indoor air pollution, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from certain building materials, is also necessary. Choosing low-VOC materials for construction and furnishings can significantly improve the quality of the air. This proactive approach to air quality ensures that occupants breathe clean and healthy air, contributing to their overall well-being and productivity.
Automation and Remote Control for Enhanced Management
Optimizing Building Performance
Automation systems play a crucial role in optimizing building performance by dynamically adjusting environmental controls based on real-time data. This intelligent approach, far exceeding manual adjustments, allows for significant energy savings. Sensors throughout the building monitor factors like temperature, humidity, and occupancy, feeding this information to the automation platform. The system then makes real-time adjustments to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, minimizing energy waste and maximizing comfort for occupants.
The ability to predict and proactively address potential issues, like impending equipment failures, is a significant advantage of this automation. This proactive maintenance strategy reduces downtime, minimizes costly repairs, and ensures the building's systems operate at peak efficiency, all contributing to long-term cost savings.
Remote Control and Monitoring
Remote control capabilities empower building managers to oversee and manage facilities from anywhere with an internet connection. This is particularly advantageous for large or geographically dispersed properties. Through intuitive dashboards and mobile applications, managers can monitor energy consumption, identify areas needing attention, and adjust settings in real-time, regardless of their physical location. This level of control provides unparalleled flexibility and responsiveness.
Real-time monitoring allows for immediate identification of anomalies and potential problems. Early detection of issues such as HVAC malfunctions or electrical surges enables swift action, minimizing disruptions and maximizing building operational efficiency. This constant oversight is critical for preventing costly breakdowns and ensuring the building's sustained performance.
Enhanced Security and Safety
Automation systems significantly enhance building security by automating access control, monitoring security systems, and managing alarm responses. Integrated systems can automatically trigger alarms and notifications in response to unauthorized access, intrusion attempts, or other security breaches, allowing for rapid responses and minimizing potential risks. This proactive approach is paramount in ensuring the safety and security of occupants and the building itself.
Remote monitoring of security systems allows for proactive security measures. Managers can monitor security cameras, access control systems, and other security measures from a central location, enabling swift response to any threats or irregularities. This vigilance, combined with automated responses, creates a robust and secure environment.
Improved Occupant Experience
Automation and remote control contribute to an improved occupant experience by optimizing comfort levels and providing personalized control over their environment. Individualized settings for temperature, lighting, and even air quality can be managed by occupants through mobile applications or dedicated interfaces, leading to a more comfortable and productive work or living space. The ability to seamlessly integrate these features into the building's management system creates a sophisticated and responsive environment.
Intelligent lighting systems and automated responses to occupancy patterns further enhance the occupant experience. By dynamically adjusting lighting based on occupancy, buildings can significantly reduce energy consumption and create a more efficient and environmentally responsible environment, while still providing a welcoming and comfortable experience for occupants.