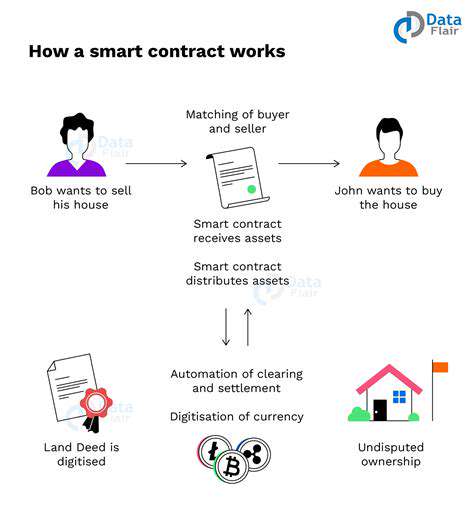
Key Benefits of Smart Contracts in Business
Improved Efficiency and Automation
Smart contracts automate various business processes, streamlining operations and significantly reducing manual intervention. This automation translates to faster transaction times, reduced errors, and a substantial decrease in administrative overhead. By eliminating the need for intermediaries in many cases, businesses can experience considerable cost savings and achieve greater operational efficiency across the board, freeing up valuable resources for more strategic initiatives.
Imagine contracts for supply chain management automatically triggering payments upon delivery confirmation or agreements for asset ownership transferring seamlessly upon meeting certain conditions. These are just two examples of how smart contracts can dramatically improve efficiency in a variety of industries, leading to a more streamlined and less error-prone business environment.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Smart contracts are inherently secure due to their immutable nature. Once deployed on a blockchain, their terms and conditions cannot be altered, ensuring trust and transparency. This inherent security minimizes the risk of fraud and disputes, providing a more reliable and trustworthy environment for business transactions. The distributed nature of blockchain technology further enhances security by distributing the record of transactions across multiple nodes, making it extremely difficult to tamper with.
Furthermore, the transparency inherent in smart contracts facilitates better accountability and trust amongst parties involved. All transactions are recorded and publicly verifiable, promoting openness and reducing the likelihood of hidden agendas or undisclosed conditions.
Reduced Costs and Increased Speed
By automating processes and eliminating intermediaries, smart contracts drastically reduce operational costs for businesses. No longer are there significant expenses associated with legal fees, transaction costs, or administrative staff to manage contracts. This leads to direct cost savings and a more profitable business model.
The speed at which transactions are processed is another significant advantage. Smart contracts can execute transactions instantly, eliminating delays inherent in traditional contract processes. This speed is crucial for businesses that require rapid response times, such as in financial markets or supply chains.
Improved Contract Management
Smart contracts offer a more efficient and secure method for managing contracts. They automate the execution of agreements, reducing the risk of human error and misunderstandings often associated with traditional contract management processes. This leads to greater clarity and fewer disputes.
Enhanced Trust and Reliability
The immutable nature of smart contracts on a blockchain fosters a high degree of trust among parties involved. The transparent and verifiable record of transactions eliminates ambiguity and strengthens relationships. This heightened trust allows for greater collaboration and reduces the need for extensive due diligence, which is crucial in international business dealings.
Greater Flexibility and Customization
Smart contracts are highly customizable and can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various business models. Their modular design allows businesses to tailor the terms and conditions to their particular requirements, creating unique and efficient contracts that streamline their workflows.
Global Reach and Accessibility
Smart contracts facilitate global transactions with ease, transcending geographical boundaries and time zones. Their decentralized nature allows for seamless transactions across borders, fostering international collaborations and expanding business opportunities globally. This accessibility is particularly valuable for businesses operating on a global scale.
Applications of Smart Contracts in Diverse Industries
Smart Contracts in Supply Chain Management
Smart contracts are revolutionizing supply chain management by automating and streamlining various processes. They can track goods from origin to destination, ensuring authenticity and verifying compliance with regulations. This automated tracking system reduces paperwork, minimizes delays, and enhances transparency. By embedding specific clauses within the contract, smart contracts can trigger actions like payments or alerts based on predefined conditions, such as the arrival of a shipment or the completion of a quality check.
Furthermore, smart contracts can facilitate secure and efficient inventory management. By automatically updating inventory levels and triggering reordering when stock falls below a certain threshold, these contracts can optimize stock levels and prevent shortages or overstocking. This leads to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency for businesses involved in the supply chain.
Smart Contracts for Financial Services
The financial services industry is another area where smart contracts are making a significant impact. They are particularly well-suited for automating tasks such as loan processing, insurance payouts, and securities trading. Smart contracts can execute these transactions automatically and securely based on pre-defined conditions, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of human error. This automation streamlines processes, reduces administrative costs, and enhances the overall speed and efficiency of financial transactions.
Cryptocurrency platforms heavily rely on smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions, automate token issuance and exchange, and enforce various conditions related to the use of digital assets. This automation ensures security, transparency, and efficiency in the handling of cryptocurrencies, fostering trust and encouraging wider adoption of blockchain technology within the financial ecosystem.
Smart Contracts in Healthcare
Smart contracts are poised to transform the healthcare industry by facilitating secure and efficient management of patient data, streamlining clinical trials, and improving drug supply chains. They can store and manage sensitive patient information securely, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations like HIPAA. This secure storage and access mechanism can enhance patient care and reduce administrative burden. Smart contracts can also automate the process of distributing and tracking medication, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of counterfeiting.
Furthermore, smart contracts can play a critical role in automating clinical trials, enabling secure data sharing and accelerating the research process. They can ensure the integrity and accuracy of data collected during trials, leading to more reliable results and potentially faster development of new treatments and medications. This increased efficiency and accountability within the healthcare system would prove beneficial to patients and researchers alike.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Smart Contracts
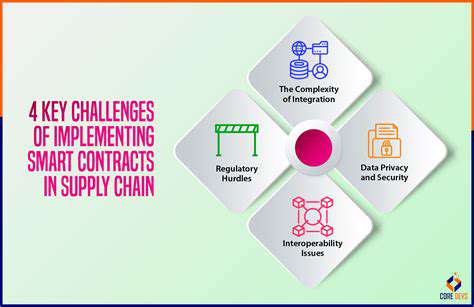
Implementing Effective I Strategies
Developing and implementing effective I strategies requires careful consideration of various factors, including organizational culture, technological advancements, and the evolving needs of the workforce. A successful strategy must be adaptable to accommodate future changes and ensure ongoing relevance. Understanding the current challenges and potential roadblocks is crucial for creating a roadmap that promotes long-term success.
This involves meticulous planning, resource allocation, and a comprehensive understanding of the desired outcomes. Effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders are essential for ensuring buy-in and minimizing resistance to change.
Addressing Workforce Skill Gaps
I initiatives often require specific skills and knowledge that may not be readily available within the existing workforce. This necessitates proactive training and development programs to equip employees with the necessary competencies. Bridging these skill gaps is crucial for successful I implementation and ensuring that employees can effectively utilize new technologies and processes.
Identifying and addressing these gaps proactively will minimize disruptions and maximize the potential of I strategies. This process should be ongoing, incorporating feedback from employees and adapting to changing technological landscapes.
Maintaining Data Security and Privacy
Implementing I strategies often involves handling sensitive data, making data security and privacy paramount. Robust security measures are essential to protect data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. Maintaining compliance with relevant regulations and industry best practices is critical to avoid legal and reputational risks.
This includes implementing strong access controls, encryption protocols, and regular security audits. Furthermore, educating employees about data security best practices is vital for preventing human error and malicious activity.
Managing Resistance to Change
Change, especially in the context of I, can often meet resistance from various stakeholders. Understanding the reasons behind this resistance is critical to navigating the challenges and developing strategies to address concerns. This could involve a lack of trust, fear of the unknown, or a perceived disruption of existing workflows.
Open communication, active listening, and providing support are essential strategies for managing resistance. Involving employees in the process and ensuring transparent communication can help build trust and acceptance of the changes involved.
Ensuring Scalability and Flexibility
I strategies must be designed with scalability and flexibility in mind. The ability to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements is vital for long-term success. This requires a robust architecture that can accommodate growth and evolution without significant disruptions.
This often involves modular design, cloud-based solutions, and adaptable software that can be scaled up or down as needed. A flexible approach allows for better response to unexpected changes and emerging opportunities.
Budgetary Constraints and Resource Allocation
I initiatives often require significant financial investment in new technologies, training, and infrastructure. Careful planning and resource allocation are critical for maximizing the return on investment (ROI) and minimizing financial risks. Realistic budgeting and prioritizing projects based on strategic value are essential for success.
This requires careful analysis of costs, benefits, and potential risks associated with various I projects. Effective project management and ongoing cost monitoring are crucial for staying within budget and achieving desired outcomes.
Measuring and Evaluating I Success
Establishing clear metrics and KPIs is essential for evaluating the success of I initiatives. Defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals is crucial for tracking progress and identifying areas for improvement. This will help to determine the effectiveness and return on investment of the implemented changes.
Regular monitoring and evaluation are essential for ensuring that I strategies remain aligned with organizational goals and objectives. This involves gathering data, analyzing results, and making necessary adjustments to maximize impact and sustainability.