IoT: Connecting the Physical World to the Digital Realm

The Rise of the Internet of Things
The IoT revolution represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with technology. From intelligent urban infrastructure to precision agriculture sensors, connected devices are creating what experts call the physical internet. What makes this transformation profound is how it bridges the gap between digital systems and tangible objects, creating feedback loops that continuously improve real-world operations.
Data Collection and Analysis
Modern IoT ecosystems generate staggering amounts of operational data - a single wind turbine can produce over 500 data points per second. The breakthrough comes in how edge computing processes this information locally, sending only relevant insights to central systems. This distributed intelligence model enables real-time decision making at unprecedented scales, whether it's adjusting traffic light patterns citywide or optimizing irrigation across thousands of acres.
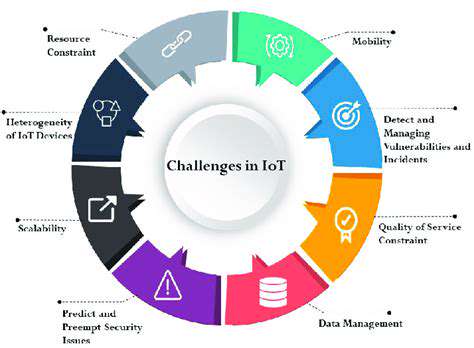
Security Concerns in IoT
As IoT networks expand, security professionals emphasize the importance of hardware-based encryption and zero-trust architectures. Recent advancements in quantum-resistant cryptography offer promising solutions for protecting critical infrastructure as computing power increases.
Applications in Smart Homes
Contemporary smart homes demonstrate IoT's potential through energy optimization systems that learn household patterns. Advanced systems now automatically adjust HVAC settings based on weather forecasts and occupancy sensors, achieving 20-30% energy savings without compromising comfort. Integrated security platforms combine motion detection, facial recognition, and anomaly detection to provide comprehensive protection.
Industrial Applications of IoT
In heavy industry, IoT enables condition-based maintenance strategies that outperform traditional schedules. Mining companies report 40% reductions in unplanned downtime by using vibration and thermal sensors to predict equipment failures. The financial impact becomes clear when considering that a single hour of production line downtime can cost manufacturers upwards of $100,000.
The Future of IoT
The next frontier involves autonomous IoT networks that self-organize and optimize. Emerging standards like Matter promise to solve interoperability challenges, while 5G networks enable massive machine-type communications. We're entering an era where IoT systems won't just report data, but will negotiate with each other to optimize broader systems, from regional power grids to global supply chains.
Optimizing Operations through Data Analytics
Data-Driven Insights for Enhanced Efficiency
Modern analytics platforms transform operational data into visual dashboards that reveal hidden opportunities. A consumer goods company recently identified a 12% energy waste pattern in their packaging line through detailed power consumption analysis. These insights become particularly valuable when correlated across multiple data streams, revealing relationships between environmental conditions, machine settings, and output quality.
Predictive Maintenance for Proactive Problem Solving
Advanced predictive models now incorporate equipment genealogy data - tracking components from manufacture through service life. This approach helped an aerospace manufacturer reduce unscheduled maintenance by 62% by identifying batches of components with higher failure probabilities based on their production history.
Improved Supply Chain Management
Digital twins of supply chains enable scenario modeling that was previously impossible. During recent port disruptions, companies using these tools rerouted shipments 30% faster than competitors. The ability to simulate alternative logistics networks provides resilience against unpredictable market shocks.
Enhanced Quality Control and Product Improvement
Computer vision systems now analyze product quality at microscopic levels while tracking defects back to specific process variables. A pharmaceutical company implemented such a system and achieved 99.99% quality consistency in tablet production, reducing waste by $2.8 million annually.
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Next-generation control systems use reinforcement learning to continuously optimize processes. In chemical manufacturing, these systems maintain ideal reaction conditions by processing thousands of data points per second, adjusting parameters in real-time to maintain perfect yields. This represents a quantum leap beyond traditional setpoint controls, delivering both quality improvements and energy savings.
The Future of Manufacturing: Enhanced Agility and Sustainability

The Rise of Automation
Collaborative robotics represent the next automation frontier, with human-robot teams achieving productivity levels neither could manage alone. In electronics assembly, these systems have reduced defect rates by 45% while increasing output. The true innovation lies in how these systems adapt to new tasks through demonstration rather than programming, significantly reducing changeover times.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Circular manufacturing models are gaining traction, with companies achieving 90% material reuse rates through advanced sorting and reprocessing systems. What makes these initiatives impactful is their economic viability - many now deliver positive ROI within 18 months through reduced material costs and premium pricing for sustainable products.
The Importance of Data Analytics
Manufacturers are adopting digital thread technologies that maintain complete product histories from design through retirement. This comprehensive data enables continuous improvement cycles that were previously impossible, with some companies reporting 30% faster iteration times on product enhancements.
Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
The additive manufacturing revolution extends beyond prototyping to full-scale production. Aerospace leaders now print fuel nozzles with internal geometries impossible to machine conventionally, achieving 40% weight reductions. What's transformative is how distributed 3D printing networks enable local production hubs, reducing logistics costs and carbon footprints simultaneously.