Immersive Learning and the Future of Education
Immersive learning environments are rapidly transforming the educational landscape, offering students engaging and interactive experiences that go beyond traditional classroom settings. These environments leverage technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) to create dynamic and personalized learning opportunities. By placing students in simulated environments, immersive learning fosters deeper understanding and retention of complex concepts. These technologies allow for exploration of abstract ideas and historical events in ways that were previously unimaginable.
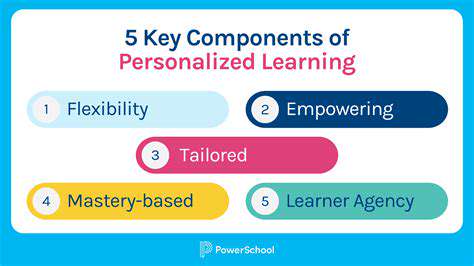
The potential benefits of immersive learning extend far beyond enhanced engagement. Personalized learning pathways can be tailored to individual student needs, maximizing learning outcomes and fostering a more inclusive educational experience. These environments can also encourage collaboration and communication among students, fostering teamwork and problem-solving skills.
Technological Advancements Driving Immersive Learning
Recent advancements in VR, AR, and MR technologies have made immersive learning more accessible and affordable. High-quality headsets and software are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling more realistic and engaging simulations. Furthermore, the development of more intuitive user interfaces and streamlined content creation tools is empowering educators to easily integrate immersive learning into their curriculum.
The widespread adoption of cloud computing and powerful processing capabilities has facilitated the creation and delivery of complex immersive experiences. This allows for the development of more interactive and personalized learning environments, accommodating diverse learning styles and needs.
Designing Effective Immersive Learning Experiences
Designing effective immersive learning experiences requires careful consideration of pedagogical principles and technological capabilities. Educators must select appropriate content and activities that align with learning objectives, while ensuring the experience is engaging and relevant to students. Clear learning goals and well-structured activities are crucial to maximizing the effectiveness of immersive learning environments.
Creating a supportive and inclusive learning environment is essential. The design process should consider accessibility features and ensure that students feel comfortable and empowered to engage fully in the learning process. This often involves incorporating diverse perspectives and promoting critical thinking skills.
The Impact on Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Immersive learning environments can significantly enhance student engagement and motivation, leading to improved learning outcomes. Students are more likely to retain information when actively involved in learning experiences, and immersive learning often facilitates such active participation. Studies have shown that students in immersive learning environments demonstrate a deeper understanding of complex concepts and a greater ability to apply their knowledge to real-world problems.
By fostering active participation and exploration, immersive learning environments promote a more holistic learning experience. This approach emphasizes critical thinking, problem-solving, and creative expression, contributing to a more well-rounded and engaged learner.
The Future of Science Education: Combining Real-World Applications with Virtual Exploration
Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice
Modern science education faces a critical challenge: effectively connecting abstract concepts with tangible, real-world applications. Students often struggle to grasp the relevance of scientific principles learned in the classroom to the problems and solutions encountered outside of the textbook. This disconnect can lead to a lack of engagement and a diminished understanding of the practical implications of scientific discoveries. To address this, educators need to actively incorporate real-world scenarios and projects into the curriculum, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation for the power of scientific inquiry.
One promising approach is to integrate hands-on experiments and projects that directly relate to current events, technological advancements, or societal issues. For example, a lesson on thermodynamics could involve designing and testing energy-efficient prototypes, while a unit on genetics could explore the ethical implications of gene editing technologies. By grounding scientific concepts in relatable contexts, students can develop a more profound understanding and a greater appreciation for the practical applications of science.
Virtual Exploration: Expanding Learning Horizons
The rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies presents exciting opportunities to revolutionize science education. Immersive virtual environments allow students to explore complex scientific phenomena in a safe and engaging manner, from the intricate workings of the human heart to the vastness of the cosmos. VR simulations can provide realistic representations of experiments, enabling students to manipulate variables and observe outcomes without the limitations of physical constraints or safety concerns.
Furthermore, virtual field trips to remote locations or historical sites can broaden students' exposure to diverse scientific contexts. Imagine taking a virtual journey to the Amazon rainforest to study biodiversity or visiting a historical laboratory to learn about past scientific discoveries. These experiences can spark curiosity and inspire a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of scientific disciplines and their impact on society.
Enhancing Engagement Through Collaborative Learning
Effective science education goes beyond individual learning and emphasizes the importance of collaborative exploration. By fostering collaborative learning environments, students can engage in peer-to-peer discussions, share ideas, and learn from one another's perspectives. Group projects, debates, and presentations can encourage critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and effective communication – all essential components of scientific literacy.
Furthermore, incorporating interactive online platforms and digital tools can facilitate collaborative learning beyond the classroom. Online forums, shared documents, and collaborative projects can connect students with experts, researchers, and other learners worldwide, creating a dynamic and engaging learning community. This approach not only enhances knowledge acquisition but also cultivates essential 21st-century skills, such as teamwork, communication, and critical thinking.