AI's Impact on Disease Classification and Prediction
AI's Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming healthcare, particularly in the area of disease classification. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of medical images, patient records, and genetic information with unprecedented speed and accuracy, potentially leading to earlier and more precise diagnoses. This ability to sift through complex data allows for the identification of subtle patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human clinicians.
By identifying these subtle patterns, AI can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy, especially for complex or rare diseases. This enhanced diagnostic capability is particularly valuable in cases where the symptoms are non-specific or where a definitive diagnosis is challenging to establish through traditional methods.
Improving Diagnostic Speed
One of the most significant benefits of AI in disease classification is its ability to accelerate the diagnostic process. AI algorithms can process information much faster than human clinicians, potentially reducing the time it takes to arrive at a diagnosis, which is crucial in situations where prompt action is essential. This speed can be especially critical in emergency situations or when dealing with life-threatening conditions.
Personalized Treatment Strategies
AI-driven disease classification can also inform the development of personalized treatment strategies. By analyzing patient-specific data, AI can identify the most effective treatment options for individual patients, taking into account their unique genetic makeup, medical history, and other relevant factors.
This personalized approach can lead to improved treatment outcomes and reduced side effects. Ultimately, it aims to optimize care for each patient, leading to better health management.
Data Integration and Analysis
Effective implementation of AI in disease classification relies heavily on the ability to integrate and analyze diverse data sources. This involves combining patient medical records, imaging data, genetic information, and other relevant factors to create a comprehensive picture of the patient's health.
The quality and completeness of this data are essential for the accuracy and reliability of AI-powered diagnostics. Robust data management systems and standardized data formats are crucial for ensuring the successful implementation of these technologies.
Addressing Limitations and Ethical Considerations
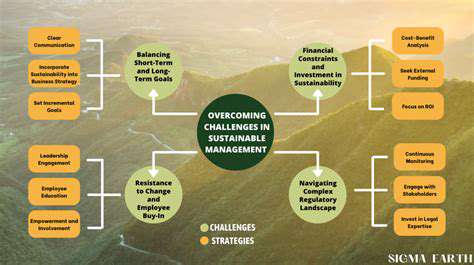
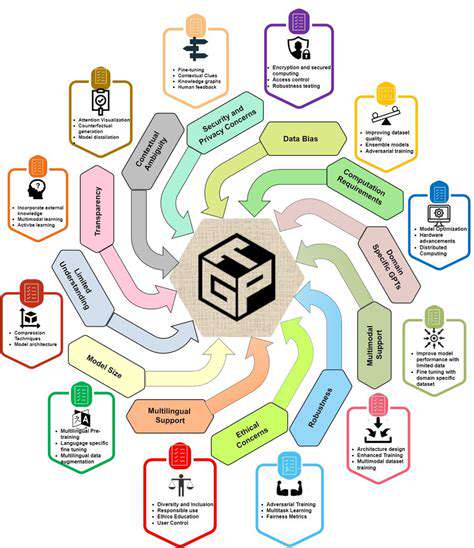
While AI holds immense promise for disease classification, it's important to acknowledge potential limitations and address associated ethical concerns. One key area is ensuring the fairness and equity of AI algorithms across different populations and demographics. Biases present in training data can lead to inaccurate or discriminatory outcomes, which must be carefully mitigated.
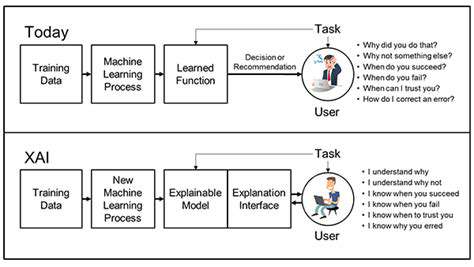
Furthermore, the interpretation and validation of AI-generated diagnoses require careful consideration. Clear guidelines and protocols are needed to ensure that AI recommendations are integrated thoughtfully into the existing clinical workflow.
Future Directions and Research
The field of AI-driven disease classification is constantly evolving, with ongoing research focusing on improving the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of these technologies. Future research will likely explore the use of AI in predicting disease risk, identifying early warning signs, and developing new diagnostic tools and therapies.
This ongoing innovation promises to further enhance healthcare capabilities and lead to a future where accurate and timely disease classification is readily available to all.
Accessibility and Cost-Effectiveness
The goal is to make AI-powered disease classification accessible and cost-effective. Reducing the barriers to implementation will be crucial for widespread adoption, ensuring that these technologies are not limited to high-resource settings. This requires ongoing efforts to develop more affordable and user-friendly AI tools and infrastructure.
Ultimately, widespread accessibility and affordability are essential for maximizing the positive impact of AI on patient care and public health outcomes.

Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
Ethical Implications of AI in Pediatric Diagnostics
The integration of AI into pediatric diagnostics raises significant ethical concerns. One crucial aspect is the potential for bias in algorithms trained on existing datasets. These datasets may reflect historical biases in healthcare, leading to inaccurate or discriminatory diagnoses, particularly for children from underrepresented populations. This issue necessitates careful curation and validation of AI models to mitigate bias and ensure equitable access to accurate diagnostic tools for all children.
Another critical ethical consideration centers around data privacy and security. AI models frequently rely on vast quantities of patient data, raising concerns about the protection of sensitive health information. Robust data security protocols and transparent data governance frameworks are essential to safeguard patient privacy and maintain trust in AI-driven diagnostic systems. This includes clear guidelines on data anonymization, access controls, and the responsible use of patient data for research and development.
Future Directions for AI in Pediatric Diagnostics
The future of AI in pediatric diagnostics holds immense promise, but realizing this potential requires ongoing research and development. One key direction involves the development of more sophisticated AI models capable of handling complex clinical scenarios and interpreting nuanced pediatric presentations. This includes creating AI systems that can integrate diverse data sources, such as clinical history, imaging results, and genetic information, to provide comprehensive and accurate diagnoses.
Further advancements should focus on creating AI tools that can personalize diagnostic recommendations based on individual patient characteristics and risk factors. This personalized approach could lead to more effective treatment strategies and improved patient outcomes. Furthermore, the development of user-friendly interfaces and educational resources for clinicians will be essential to facilitate the seamless integration of AI into routine pediatric diagnostic workflows.
Addressing Challenges and Ensuring Accessibility
To ensure the successful implementation of AI in pediatric diagnostics, addressing the challenges related to data availability, model validation, and regulatory frameworks is crucial. Efforts should focus on building large, diverse, and high-quality datasets of pediatric medical images and clinical records to train robust and accurate AI models. Rigorous validation studies and clinical trials are needed to establish the safety and efficacy of these models before widespread adoption. Moreover, clear and comprehensive guidelines and regulations for the development, deployment, and use of AI in pediatric diagnostics will be necessary to ensure patient safety and public trust.
Ensuring equitable access to AI-powered diagnostic tools is paramount. Efforts should be made to bridge the digital divide and provide training and support for clinicians to effectively utilize these tools. This will require collaborations between technology developers, healthcare providers, and policymakers to develop sustainable and accessible solutions that can benefit all children, regardless of their socioeconomic background or geographic location.