Streamlining Payment Processes and Risk Management

Optimizing Payment Infrastructure
Payment systems form the financial backbone of any business. Modern solutions offer scalability that traditional systems can't match, adapting easily to fluctuating transaction volumes. Security remains paramount, with advanced encryption now standard for protecting sensitive financial data during transmission and storage.
Selecting payment partners requires careful vetting. The ideal provider balances reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness, offering robust fraud prevention without excessive fees. Businesses should prioritize solutions that integrate seamlessly with their existing accounting and CRM platforms to minimize reconciliation headaches.
Improving Customer Experience
Checkout friction remains a major cause of abandoned carts. Streamlined payment flows that remember customer preferences and auto-fill repeat information can dramatically improve completion rates. Offering localized payment options that match regional preferences demonstrates understanding of customer needs.
Transparent pricing builds trust. Clearly displaying all fees upfront prevents unpleasant surprises that damage customer relationships. Well-designed payment interfaces guide users effortlessly through the process with intelligent error prevention and helpful tooltips where needed.
Enhancing Security Protocols
Cyber threats evolve constantly, requiring proactive defense strategies. Beyond basic encryption, behavioral analytics can detect anomalous patterns that indicate potential fraud. Regular security audits help identify vulnerabilities before criminals exploit them, while employee training reduces human error risks.
Tokenization provides additional protection by replacing sensitive data with unique identifiers. This ensures that even if systems are compromised, actual financial details remain secure. Multi-factor authentication adds another layer of protection for high-value transactions.
Reducing Processing Times
Slow payments create cash flow bottlenecks. Optimizing authorization pathways and minimizing manual approval layers can accelerate funds availability significantly. Intelligent routing algorithms direct transactions through the fastest available channels based on real-time network conditions.
Automated exception handling prevents minor issues from causing major delays. Systems can now flag and resolve common problems like mismatched addresses without human intervention, keeping payments moving smoothly.
Minimizing Transaction Costs
Payment processing fees accumulate quickly at scale. Volume discounts and interchange-plus pricing models can yield substantial savings for high-transaction businesses. Analyzing payment mix reveals opportunities to steer customers toward lower-cost options through strategic incentives.
Consolidating processors reduces administrative overhead. Rather than maintaining multiple vendor relationships, businesses can often achieve better rates and simplified reporting by concentrating volume with a single provider that meets all needs.
Integrating with Existing Systems
Payment solutions shouldn't require operational overhauls. Modern APIs enable seamless connectivity with ERP, accounting, and inventory systems, automatically syncing transaction data across platforms. Thorough testing ensures new implementations don't disrupt critical workflows.
Phased rollouts mitigate transition risks. Starting with pilot groups allows for issue identification and resolution before company-wide deployment. Comprehensive training materials and responsive support ease adoption across departments with varying technical proficiency.
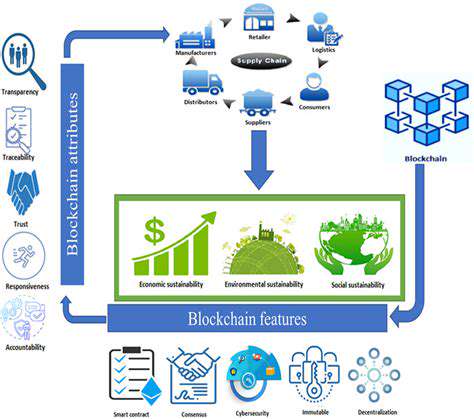
The Future of Supply Chain Finance on the Blockchain
The Rise of Digitalization
Digital transformation enables supply chain participants to share information securely in real time. Blockchain's distributed ledger technology provides an immutable record of transactions, reducing disputes and enabling faster reconciliation. Smart contracts automate payment triggers when predefined conditions are met, eliminating manual processes.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Visibility across the supply network allows partners to coordinate more effectively. Shared dashboards provide real-time inventory tracking and demand signals, enabling just-in-time production adjustments. This collaborative approach reduces bullwhip effects where small demand fluctuations amplify up the supply chain.
AI-Powered Insights and Predictions
Machine learning algorithms analyze patterns across vast datasets that humans can't process. These systems can predict component shortages or transportation delays weeks in advance, allowing proactive mitigation. Prescriptive analytics recommend optimal responses, balancing cost, speed, and reliability considerations.
Sustainable Practices and Ethical Considerations
Consumers increasingly demand responsibly sourced products. Blockchain enables end-to-end provenance tracking, verifying sustainable practices from raw materials to finished goods. Ethical financing models incentivize suppliers to meet environmental and social standards through preferential terms.
Increased Focus on Risk Management
Geopolitical instability and climate change introduce new vulnerabilities. Advanced scenario modeling helps organizations stress-test their supply networks against potential disruptions, developing contingency plans for various failure modes. Diversified supplier bases and alternative logistics routes provide resilience.
Financial Inclusion and Access to Capital
Blockchain-based financing platforms connect small suppliers directly with investors, bypassing traditional credit barriers. Invoice tokenization allows fractional ownership of receivables, creating liquidity for businesses that previously waited months for payment. This democratization of capital benefits entire supply ecosystems.
The Role of Technology in Streamlining Processes
Emerging technologies converge to create seamless supply chain finance solutions. IoT sensors provide real-time asset tracking, while AI optimizes routing and inventory placement. These integrated systems create self-adjusting supply networks that respond autonomously to changing conditions, minimizing human intervention.