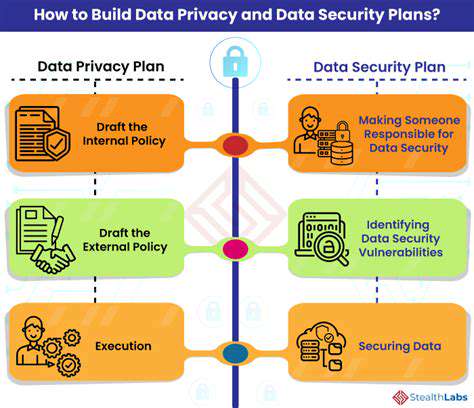
Identifying Key Predictors of Student Success
Predictive modeling in education aims to identify factors that significantly correlate with student success. These factors can range from academic performance in previous grades to socioeconomic background, attendance rates, and even engagement in extracurricular activities. By analyzing historical data and identifying these key predictors, educators can gain valuable insights into the multifaceted influences on student achievement, moving beyond a simple focus on test scores alone.
Careful consideration must be given to the ethical implications of using predictive models. While these models can reveal valuable insights, they should not be used to perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequalities. Data collection and analysis must be conducted in a way that respects student privacy and avoids reinforcing harmful stereotypes. A crucial step is ensuring that the models are not disproportionately impacting specific student populations.
Utilizing Data from Multiple Sources
Effective predictive models often incorporate data from diverse sources. This can include student grades, attendance records, standardized test scores, teacher evaluations, and even information on family demographics and socioeconomic status. By combining data from various sources, educators can construct a more comprehensive picture of each student's learning context and identify potential challenges or strengths.
Integrating data from multiple sources, however, also presents challenges. Data quality, consistency, and potential biases need careful scrutiny. Incorporating data from different systems and formats requires significant technical expertise and careful data cleaning and transformation procedures to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Developing and Validating Predictive Models
The process of building a predictive model involves selecting appropriate algorithms, training the model on historical data, and then evaluating its performance. Different algorithms, such as regression models, decision trees, or machine learning techniques, have varying strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on the specific characteristics of the data and the desired outcomes. Thorough validation is essential to ensure the model's accuracy and generalizability to new datasets.
Interpreting Model Outputs and Actionable Insights
Understanding the output of a predictive model is crucial for deriving meaningful insights and developing targeted interventions. The model's predictions should be interpreted in the context of the specific student's circumstances, and educators should avoid drawing simplistic conclusions. The goal is to identify potential challenges and offer tailored support, not to label students or perpetuate stereotypes.
Implementing Interventions Based on Predictions
Predictive modeling offers a powerful tool for proactively addressing potential learning difficulties. By identifying students who are at risk of falling behind, educators can implement early interventions and support systems. These interventions can range from targeted tutoring, extra academic assistance, or specialized counseling, based on the specific needs revealed by the model. The focus should be on providing individualized support and creating a learning environment conducive to success for all students.
Ethical Considerations and Bias Mitigation
It is critical to acknowledge the potential for bias in predictive models. Historical data may reflect existing inequalities, and if not addressed, these biases can be perpetuated and amplified by the model. Careful consideration must be given to the potential impact of these models on different student populations, and steps should be taken to mitigate bias during data collection, model development, and interpretation. Transparency and ongoing evaluation are crucial to ensure the model's fairness and equity.
Regular audits of the model's performance and impact on different student groups are essential. This allows for adjustments and modifications to be made as needed, ensuring that the model remains fair, accurate, and beneficial to all students. Ethical guidelines and protocols should be established to ensure responsible use and avoid any unintended negative consequences.
Identifying and Enhancing Effective Teaching Practices

Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Effective performance management hinges on the precise identification of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). These metrics provide a quantifiable way to track progress towards strategic goals. Choosing the right KPIs is crucial, as they must align directly with the objectives of the team or individual being assessed. This ensures that efforts are focused on activities that truly contribute to overall success.
A well-defined KPI framework also helps in establishing clear expectations and fostering a culture of accountability. By understanding what constitutes success, team members can better direct their efforts and track their progress. This ultimately leads to improved performance and more efficient use of resources.
Understanding the Context of Performance
Performance is not isolated; it's deeply intertwined with the surrounding context. Factors like industry trends, market conditions, and internal organizational changes all play a role in shaping individual and team performance. Understanding these influencing factors is vital for accurate assessment.
Analyzing the broader context helps avoid misinterpretations and ensures that performance evaluations are comprehensive and fair. This multifaceted approach promotes a more nuanced understanding of the drivers behind observed performance levels.
Establishing Clear Performance Goals
Clear and measurable goals are essential for motivating individuals and teams and providing a roadmap to success. These goals should be specific, time-bound, achievable, relevant, and measurable (SMART). This structure ensures that everyone is working towards the same objectives and understands the expected outcomes.
Well-defined goals provide a clear target for performance improvement. They enable individuals to focus their efforts and track progress effectively, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
Developing Effective Feedback Mechanisms
Regular and constructive feedback is paramount for performance enhancement. Feedback should be specific, timely, and focused on actionable steps for improvement. It's important to provide both positive reinforcement for successes and constructive criticism for areas needing attention. This two-sided approach fosters a growth mindset.
Creating a safe and open environment for feedback exchange is critical. It encourages open communication and allows for continuous improvement. This fosters a culture of learning and development within the team or organization.
Implementing Performance Improvement Strategies
Performance enhancement requires a proactive approach, not just reactive responses to underperformance. Strategies must be tailored to individual or team needs, taking into account the specific challenges and opportunities they face. Effective strategies address the root causes of performance issues, aiming for sustainable improvements rather than short-term fixes.
Implementing these strategies requires careful planning and execution. It is crucial to monitor progress and adjust strategies as needed to ensure they remain aligned with organizational goals and individual needs.
Utilizing Technology for Performance Management
Technology plays an increasingly important role in modern performance management. Performance management systems and software can streamline processes, track progress, and provide valuable insights. Utilizing these tools can improve efficiency and allow for more data-driven decision-making.
Technological advancements provide more sophisticated ways to monitor and analyze performance. This allows for a more precise understanding of individual and team contributions and facilitates targeted interventions.
Measuring and Tracking Performance Results
Regular measurement and tracking are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of performance improvement initiatives. This process involves collecting data, analyzing trends, and identifying areas for further development. Data-driven insights provide valuable information for strategic decision-making.
Tracking performance metrics allows for adjustments in strategies and resource allocation, ensuring that efforts remain focused on achieving optimal outcomes. This iterative process ensures that performance management is a dynamic and evolving process that adapts to changing needs.