Autonomous Operations and Enhanced Flexibility
Autonomous Vehicle Navigation
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on sophisticated navigation systems to perceive and interpret their surroundings. These systems utilize a combination of sensors, including cameras, lidar, and radar, to create a detailed 3D map of the environment. This data is then processed by advanced algorithms that enable the vehicle to understand its position, identify obstacles, and make safe driving decisions. The accuracy and reliability of this perception system are crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation in various traffic conditions.
The navigation algorithms must be robust enough to handle dynamic situations, such as unexpected obstacles or changes in traffic patterns. This requires sophisticated machine learning models that can adapt to new information in real-time. Furthermore, the systems need to be constantly updated to maintain their effectiveness in evolving environments.
Enhanced Safety Features
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are integral to enhancing the safety of autonomous operations. These systems can detect potential hazards, such as pedestrians or cyclists, and automatically initiate braking or steering maneuvers to prevent accidents. The inclusion of these systems significantly reduces the risk of collisions and promotes safer driving practices.
Beyond basic collision avoidance, advanced safety features can also include systems that monitor driver fatigue and alert the system to potential issues. Such proactive safety measures, combined with the enhanced perception capabilities of autonomous vehicles, contribute to a safer and more reliable transportation experience for everyone.
Autonomous braking systems, for example, are designed to react faster and more accurately than human drivers, minimizing the chances of collisions and reducing the severity of impacts when collisions are unavoidable.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
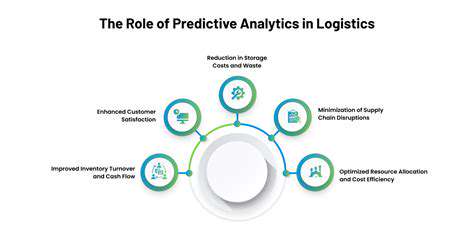
Autonomous operations offer significant potential for improving efficiency and productivity in various industries. By automating transportation tasks, these systems can reduce operational costs, optimize routes, and increase overall throughput. This is particularly valuable in logistics, delivery services, and other sectors where transportation plays a vital role.
Autonomous vehicles can operate 24/7 without the need for rest breaks, leading to increased availability and reduced downtime. This continuous operation significantly enhances the productivity of transportation networks. The ability to optimize routes and adapt to real-time traffic conditions further enhances efficiency, reducing travel time and fuel consumption.
Furthermore, autonomous operations can lead to more predictable and reliable delivery schedules, improving customer satisfaction and enabling businesses to better manage their operations. The integration of autonomous technology has the potential to revolutionize many industries.
The Future of Smart Factories: Beyond the Factory Walls

The Rise of AI-Powered Automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize the manufacturing landscape, transforming smart factories into truly intelligent entities. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including sensors, machine learning models, and human input, to optimize production processes and predict potential issues before they arise. This proactive approach to problem-solving ensures greater efficiency and reduces downtime, leading to significant cost savings and improved output.
Predictive Maintenance and Proactive Repair
Smart sensors embedded within machinery continuously monitor operational parameters, providing real-time data for analysis by AI systems. Predictive maintenance algorithms can identify subtle patterns indicative of potential equipment failures, enabling proactive interventions to prevent costly breakdowns. This capability ensures consistent production and minimizes disruptions.
By preventing costly and time-consuming repairs, businesses can significantly reduce maintenance costs and improve operational reliability.
Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization
Real-time data sharing across the entire supply chain, facilitated by smart technologies, provides unprecedented visibility into material flow, inventory levels, and delivery schedules. This visibility enables companies to optimize their supply chains, ensuring timely delivery of materials and minimizing potential bottlenecks. The ability to anticipate potential disruptions allows companies to proactively adjust their strategies, ensuring uninterrupted production.
Improved Quality Control and Defect Prevention
Advanced vision systems and machine learning algorithms can identify defects in products with remarkable accuracy, significantly enhancing quality control processes. This capability reduces the rate of defective products, resulting in higher product quality and minimizing waste. Moreover, these sophisticated systems can identify trends in defects, enabling companies to address root causes and improve manufacturing processes.
The Importance of Data Security and Privacy
The increasing reliance on data in smart factories necessitates robust data security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Comprehensive security protocols must be implemented to safeguard intellectual property, operational data, and customer information. Ensuring data privacy is critical for maintaining trust and compliance with regulatory requirements.
The Need for Skilled Workforce Development
The integration of smart technologies in factories necessitates a skilled workforce that can operate, maintain, and manage these systems. Investing in training programs and upskilling initiatives is crucial to equip workers with the necessary skills for the future of work. Companies must embrace a culture of continuous learning to ensure that their employees possess the knowledge and expertise needed to thrive in the changing landscape of smart factories.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Smart factories have the potential to significantly reduce their environmental footprint by optimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and implementing sustainable practices. Integrating green technologies and optimizing resource utilization are key elements in achieving environmentally responsible production. The focus on sustainability is not just a trend, but a necessity for long-term profitability and societal well-being.