Edge Computing: Processing at the Source

Edge Computing: A Decentralized Approach
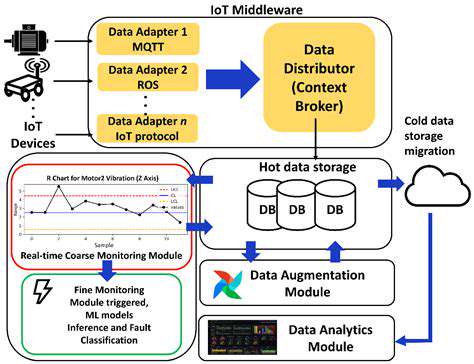
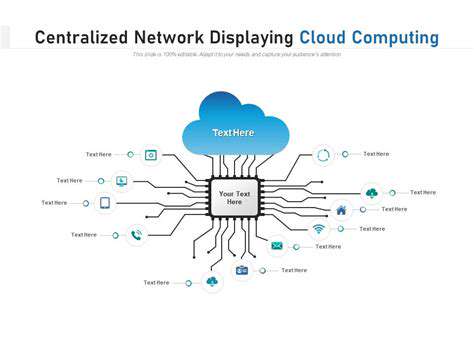
Edge computing represents a paradigm shift in data handling and utilization. Rather than depending entirely on distant centralized data centers, edge computing positions processing capabilities nearer to where data originates. This decentralized model delivers multiple advantages, such as minimized delays and enhanced responsiveness. Such a distributed framework is indispensable for applications requiring instant processing and minimal delay interactions. Additionally, it bolsters data security and privacy by restricting the transfer of sensitive information across potentially insecure networks.
Benefits of Processing at the Edge
A primary benefit of edge computing lies in its capacity to drastically cut down latency. Processing data near its source allows applications to react almost instantaneously to events and user inputs. This immediate response capability is vital for applications such as self-driving cars, industrial automation systems, and interactive gaming platforms. Moreover, edge computing strengthens data security by reducing the exposure of sensitive data during transmission across networks.
Another notable advantage is the optimized use of resources. By handling data locally, edge computing alleviates the burden on centralized data centers and enhances network efficiency. This proves especially beneficial for applications generating large volumes of data.
Challenges in Implementing Edge Computing
Despite its benefits, deploying edge computing comes with hurdles. A major obstacle is the expense of installing and maintaining edge devices across multiple locations. Additionally, overseeing and securing a network of distributed edge devices can be intricate. Maintaining uniform security measures and data consistency across diverse edge nodes is a paramount concern.
Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing finds utility across various sectors. In manufacturing, it facilitates real-time oversight and operation of equipment, boosting productivity and reducing interruptions. In healthcare, it allows medical data processing closer to patients, enabling quicker diagnoses and treatments. This local processing is particularly beneficial in rural or resource-limited areas.
Future of Edge Computing
The prospects for edge computing are bright. Emerging technologies like 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) are fueling demand for edge computing solutions. With escalating data volumes and the need for real-time applications, edge computing will increasingly influence technological progress. Anticipate deeper integration of edge computing into everyday life, from intelligent home systems to autonomous transportation. The advancement of edge computing is poised to spur further innovation across multiple domains.
Key Differences in Latency and Speed
Latency: A Critical Distinction
Latency, or the delay in data transmission from source to destination, plays a pivotal role in applications needing swift responses. Cloud computing, dependent on geographically dispersed data centers, typically experiences higher latency compared to edge computing since data traverses longer distances to cloud servers and back. Edge computing, by processing data locally, slashes latency, making it perfect for applications like live video streaming or autonomous vehicle navigation requiring near-instant feedback.
Grasping latency is essential when deciding between edge and cloud computing. The balance between speed, storage, and processing power becomes evident when latency is a key factor. Edge computing is superior in low-latency contexts, whereas cloud computing may be better suited for tasks needing extensive storage or computational power, even with higher latency.
Processing Power: Local vs. Centralized
Edge computing utilizes processing power spread across the network. This setup allows local data processing, diminishing the necessity to transmit data to a central site. Such localized processing can markedly enhance performance in scenarios demanding real-time analysis, like industrial automation or IoT devices.
Conversely, cloud computing depends on centralized, high-capacity server infrastructure for processing. This provides substantial computational power when required, but the physical distance between users and servers can introduce delays. Cloud computing is ideal for tasks requiring heavy computation, such as big data analytics or complex simulations.
Data Security: Localized Protection
Edge computing's decentralized nature offers a distinct security benefit. Data processed locally reduces the risks associated with transmitting sensitive information over long distances to cloud servers. This approach adds a security layer, especially crucial for sectors like finance or healthcare dealing with sensitive data.
While cloud services implement strong security protocols, the inherent risks of data transmission are mitigated in edge computing. This is particularly relevant in areas with limited or unstable network connectivity, where data interception or breaches are more probable.
Scalability: Adapting to Growing Demands
Cloud computing generally offers superior scalability. Resources can be swiftly adjusted to meet varying workloads, making it suitable for applications with unpredictable needs. However, scaling edge computing infrastructure can be more challenging and costly, depending on deployment specifics.
Scaling edge computing effectively demands meticulous planning and management of the distributed network to ensure resources align with demand fluctuations. The decentralized nature of edge networks may necessitate more sophisticated scaling solutions compared to the centralized cloud.
Cost Considerations: Balancing Investment and Efficiency
Edge computing may require a higher initial investment than cloud computing, especially for widespread deployments. Yet, the reduced latency and enhanced efficiency of edge computing can yield long-term savings in certain scenarios. For example, local data processing can lower bandwidth expenses.
Cloud computing's pay-as-you-go model typically involves lower upfront costs. However, expenses related to data transfer, cloud processing, and potential latency issues may accumulate over time, possibly offsetting the initial cost advantage.
Maintenance and Management: Localized vs. Centralized
Managing a distributed edge computing network can be more complex than overseeing a centralized cloud setup. Maintaining and updating numerous edge devices requires robust remote monitoring and automated update mechanisms, demanding advanced management tools and expertise.
Cloud computing's centralized infrastructure simplifies maintenance, with providers handling updates and upkeep, reducing user burden. However, dependence on third-party providers may introduce data control limitations.
Specific Use Cases: Where Each Shines
Edge computing excels in real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and live video streaming, where low latency is critical for seamless operation.
Cloud computing is ideal for applications needing vast storage, complex processing, or large-scale data analysis, benefiting from the cloud's extensive resources.
Cost Considerations and Scalability
Initial Investment Costs
Cloud computing typically involves lower initial costs, as users pay only for the resources they consume. This is advantageous for startups or businesses with variable needs, eliminating hefty upfront infrastructure investments. However, unexpected usage surges can lead to higher long-term expenses.
Edge computing requires a more substantial initial outlay for hardware and possibly specialized software. This cost can be significant, especially for multi-location deployments. Nevertheless, the potential for reduced latency and improved security may result in long-term savings by optimizing data processing and cutting bandwidth costs.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing's scalability is a major draw, enabling easy adjustment of resources to match demand. This flexibility is invaluable for businesses with unpredictable workloads or rapid growth, allowing scaling without significant capital investment.
Edge computing's scalability is more complex. While edge devices can be added or removed, scaling across a vast network is more intricate and costly compared to the cloud's elasticity. However, edge computing provides more consistent performance for real-time and critical applications.
Bandwidth Costs and Data Transfer
Cloud computing depends on continuous data transfer to and from the cloud, which can incur substantial bandwidth costs, particularly for high-volume data processing. These expenses can escalate if data volumes are large and transfer distances are extensive.
Maintenance and Support Costs
Cloud computing often includes managed services, easing maintenance and reducing internal IT workload. Providers handle infrastructure upkeep and security updates, letting businesses focus on core operations. However, reliance on third-party support may introduce vulnerabilities and dependencies.
Long-Term Operational Costs
Edge computing, despite higher initial costs, can lead to long-term savings through reduced bandwidth usage and latency. Local data processing minimizes the need to transfer large datasets to the cloud, lowering bandwidth fees and improving operational efficiency. However, ongoing maintenance of edge devices and networks must be carefully managed.