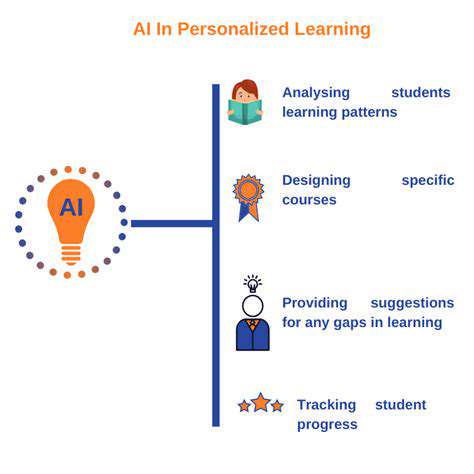
Understanding the Concept of Bias
AI systems, while powerful, are not immune to the biases present in the data they are trained on. This means that if the data reflects existing societal prejudices or stereotypes, the AI system will likely perpetuate and even amplify those biases in its outputs. Understanding this fundamental connection between data and AI bias is crucial for responsible development and deployment. Recognizing the potential for bias is the first step towards mitigating its impact.
Bias in AI manifests in various forms, ranging from gender and racial stereotypes to socioeconomic disparities. These biases can have significant consequences, impacting everything from loan applications to criminal justice assessments, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes.
Data Collection and Representation
The data used to train AI systems is fundamental to their performance and, critically, to the absence or presence of bias. If the dataset is not representative of the population it aims to serve, the AI system will likely reflect and amplify the biases inherent in the limited data. For instance, if a facial recognition system is trained predominantly on images of light-skinned individuals, it will likely perform poorly on images of individuals with darker skin tones.
Careful consideration must be given to the diversity and representativeness of the data used to train AI models. The process of data collection and selection should be meticulously scrutinized to identify and address potential biases. Ensuring comprehensive and balanced datasets is a crucial step towards creating fairer and more equitable AI systems.
Algorithmic Design and Implementation
The algorithms themselves can also introduce or exacerbate biases. For example, some algorithms may be inherently prone to reinforcing existing inequalities if not designed and implemented with careful attention to fairness considerations. A crucial aspect of algorithmic design is to identify and eliminate any potential for discrimination. This requires a deep understanding of the potential biases embedded within the algorithms and proactive steps to mitigate them during the development process.
Evaluating and Monitoring AI Systems
Regular evaluation and ongoing monitoring of AI systems are essential to identify and address any emerging biases. Continuous evaluation can help detect subtle biases that may not be apparent during initial testing. This process should incorporate diverse perspectives and involve regular feedback loops to ensure that the AI system remains fair and equitable in its application across various contexts.
Implementing robust evaluation methodologies and monitoring tools is vital for detecting and addressing bias throughout the lifecycle of the AI system. This includes evaluating the system's performance on different demographic groups and proactively addressing any discrepancies that may emerge.
Addressing Bias in Real-World Applications
The impact of AI bias extends far beyond theoretical concerns; it directly affects real-world outcomes. Addressing these biases in practical applications, such as loan approvals or hiring processes, requires a multifaceted approach. This involves not only refining algorithms but also educating stakeholders, establishing ethical guidelines, and ensuring transparency in how AI systems operate.
Ultimately, mitigating bias in AI systems requires a collaborative effort from researchers, developers, policymakers, and the broader community. This collective responsibility is paramount to ensuring that AI systems are used responsibly and equitably to benefit society as a whole.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations and Standards

Understanding Regulatory Frameworks
Comprehending the nuances of regulatory frameworks is crucial for any organization seeking to operate within legal boundaries. This involves a deep dive into the specific regulations applicable to your industry and geographic location. Failure to grasp these complexities can lead to significant penalties and reputational damage. Understanding the various interpretations and potential grey areas within the framework is also essential.
Implementing Robust Compliance Procedures
Implementing robust and comprehensive compliance procedures is a critical step. These procedures should cover all aspects of your operations, from record-keeping to employee training and communication. Effective compliance procedures provide a clear roadmap for employees to follow and ensure consistent adherence to regulations. Regular reviews and updates of these procedures are vital, given the dynamic nature of regulatory landscapes.
Regular Training and Education
Regular training and education programs for employees are essential to foster a culture of compliance. Employees need to understand the regulations and their responsibilities within the framework. This includes not only initial training but also ongoing updates and refresher courses to address changes in regulations and best practices. These training programs should be tailored to specific roles and responsibilities, ensuring employees are equipped to make informed decisions.
Establishing Clear Communication Channels
Establishing clear and accessible communication channels for reporting potential compliance issues is paramount. This includes designated individuals or departments for receiving and investigating reported concerns. Open communication fosters a safe environment where employees feel empowered to report potential violations without fear of retribution. This trust is vital to maintaining a strong compliance record.
Conducting Regular Audits and Assessments
Regular audits and assessments are crucial to identify potential gaps in compliance procedures. These assessments should cover all areas of operation, including policies, procedures, and employee conduct. Identifying these gaps early on allows for proactive corrective actions, mitigating potential risks and ensuring ongoing adherence to regulations. This proactive approach is much more cost-effective than reactive measures.
Maintaining Accurate Records and Documentation
Maintaining accurate and detailed records and documentation is an essential component of compliance. This includes maintaining records of all transactions, communications, and decisions. Thorough documentation provides a clear audit trail and strengthens the organization's ability to demonstrate compliance when needed. This documentation is critical in addressing potential issues or inquiries from regulatory bodies.
Seeking Expert Advice and Guidance
Seeking expert legal and compliance advice is often a necessary step. Consultations with legal professionals or compliance experts can provide tailored guidance based on specific organizational needs and regulatory requirements. This external expertise can help you avoid costly mistakes and develop the most effective strategies for maintaining compliance. Staying abreast of the latest regulatory changes is best achieved with expert guidance.
Key Features and Functionality of AI Auditing Tools
Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency
AI auditing tools leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets with unparalleled speed and precision, significantly reducing the time and resources required for traditional audits. This enhanced efficiency translates to quicker turnaround times, allowing organizations to respond more rapidly to emerging risks and regulatory changes. The accuracy of these tools often surpasses human capabilities when dealing with complex data patterns, leading to more reliable identification of anomalies and potential issues.
Furthermore, AI-powered systems can automate repetitive tasks, such as data validation and pattern recognition, freeing up human auditors to focus on more complex, strategic analyses. This shift in focus allows for a deeper understanding of the underlying causes of potential problems and the development of more effective mitigation strategies. The combination of speed, accuracy, and automation makes AI auditing tools a critical asset for organizations seeking to maintain compliance and improve operational efficiency.
Improved Compliance and Risk Management
AI auditing tools play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with various regulations and standards by automatically identifying potential violations or discrepancies. This automated process significantly reduces the risk of human error and oversight, leading to greater confidence in the accuracy and completeness of the audit findings. Early detection of compliance issues allows organizations to take proactive measures to rectify them, thereby minimizing potential penalties and reputational damage.
Beyond compliance, these tools excel at proactively identifying and assessing various operational risks. By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI auditing systems can pinpoint potential vulnerabilities and areas of concern. This predictive capability enables organizations to implement preventative measures and strengthen their risk management strategies. Ultimately, these tools empower organizations to operate more securely and responsibly, mitigating potential financial losses and maintaining a strong reputation within the industry.
AI auditing tools are also invaluable in identifying and mitigating financial risks, such as fraud and misappropriation of funds. Their ability to analyze large volumes of data allows for the rapid detection of unusual transactions and patterns that might otherwise be missed by human auditors. This proactive approach enhances the overall security posture of an organization and safeguards against potential financial losses. By implementing AI-powered auditing tools, organizations can effectively streamline their risk management procedures and enhance their ability to identify and address emerging threats.
The integration of AI into the auditing process fosters a culture of continuous improvement and enhanced risk management practices, ultimately contributing to the long-term sustainability and success of the organization.
By automating the identification of potential issues, AI tools allow for a more comprehensive and thorough review of financial records and operational procedures.