Introduction to Edge Computing in Smart Cities
Understanding the Core Concept
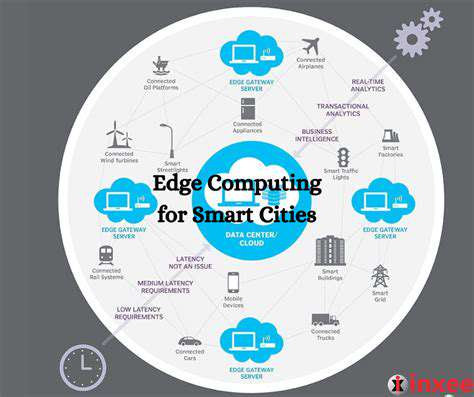
Modern edge computing represents a fundamental transformation in data handling methodologies. Rather than relying exclusively on centralized cloud servers, computational tasks now occur nearer to where data originates. This proximity-driven approach dramatically cuts delays and enhances operational speeds - a vital feature for time-critical implementations.
This decentralized framework enables sensors and devices to conduct immediate processing without persistent dependence on remote data centers. Edge systems typically refine and consolidate information before cloud transmission, substantially decreasing data volumes while reducing associated storage and bandwidth expenses.
Key Benefits of Edge Computing
Perhaps the most notable benefit lies in performance optimization. Localized data processing allows near-instantaneous system responses, creating superior user interactions and operational efficiency. Such capabilities prove indispensable for autonomous transportation networks, industrial control systems, and live multimedia distribution.
Minimizing processing delays forms the cornerstone of edge computing's competitive advantage. The technology facilitates accelerated operational decisions and more dynamic applications. Additionally, preliminary data handling at source locations decreases transmission expenses and cloud storage requirements.
Security protocols benefit significantly through localized data retention near generation points. This geographical containment strategy mitigates exposure risks during extended data transfers across networks.
Applications Across Various Industries
Edge computing demonstrates remarkable versatility across multiple sectors. Industrial operations, medical services, and urban infrastructure all experience transformative impacts from these technological advancements.
Manufacturing environments utilize edge devices for continuous equipment surveillance, enabling preemptive maintenance and operational continuity. Healthcare providers process diagnostic imagery and patient records locally, achieving swifter medical evaluations and therapeutic strategies.
Municipal authorities implement edge solutions for dynamic transportation coordination, energy management optimization, and enhanced community safety measures.
Challenges and Considerations
While offering substantial benefits, edge computing introduces several implementation complexities. Establishing reliable infrastructure to support distributed device networks demands significant investment. This includes developing secure communication standards and safeguarding edge-stored information.
Managing extensive edge device networks presents substantial logistical hurdles. Maintaining peak performance and security requires advanced monitoring systems and efficient administrative protocols.
Incorporating edge solutions into legacy systems often proves challenging, necessitating meticulous strategizing to ensure harmonious system integration without service interruptions.
Future Trends and Developments
Edge computing continues advancing rapidly through continuous technological innovation. Progress in hardware miniaturization and cost reduction accelerates adoption rates, while artificial intelligence enhancements enable more complex edge-based analytics.
The convergence with 5G networks and similar high-speed connectivity solutions drives exponential growth in edge implementation. These developments facilitate increasingly sophisticated edge applications across diverse environments.
Security and privacy considerations remain paramount, with ongoing emphasis on advanced encryption methods and protected communication channels for sensitive edge-processed data.
Enabling Scalable and Sustainable Smart City Solutions

Optimizing Resource Allocation
Strategic resource distribution forms the foundation for scalable, sustainable operations. Comprehensive analysis of current usage patterns identifies inefficiencies, enabling targeted optimization across organizational functions. Process refinement and redundancy elimination generate substantial cost reductions while boosting productivity metrics. This forward-looking methodology ensures resources meet present requirements while accommodating future expansion. Detailed operational understanding permits preemptive adjustments, preventing workflow disruptions.
Effective resource management additionally requires cultivating organizational accountability. Transparent communication structures, well-defined responsibilities, and measurable performance indicators ensure collective awareness of resource utilization priorities. This framework empowers personnel to make judicious allocation decisions, reducing inefficiencies while maximizing output. A robust resource governance model promotes responsible usage at all organizational levels.
Developing Sustainable Practices
Comprehensive sustainability transcends mere resource optimization, encompassing environmental stewardship, ethical procurement, and long-term operational resilience. Sustainable transformation represents not temporary adaptation but fundamental organizational evolution with lasting ecological and social benefits. Priority initiatives include renewable energy adoption, carbon emission reduction, and waste minimization protocols.
Ethical sourcing commitments ensure materials procurement respects environmental and community welfare, strengthening stakeholder trust and brand integrity. Responsible business practices demonstrate genuine commitment to positive societal impact while ensuring operational longevity.
Sustainable infrastructure investments constitute another critical component. Energy-efficient technologies, circular economic principles, and innovative waste processing solutions collectively reduce environmental footprints while generating long-term financial benefits. Forward-looking sustainability strategies position organizations for enduring success amidst evolving ecological and economic landscapes.
Holistic sustainability extends to workforce welfare and community relations. Inclusive workplace environments, professional development opportunities, and local community support all contribute to comprehensive sustainability programs.