Edge Computing: A Decentralized Approach
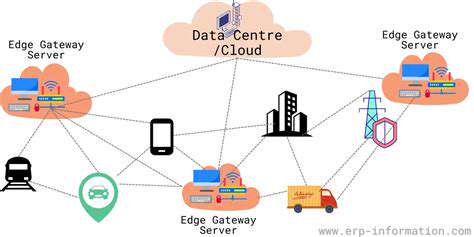
Edge computing, a distributed computing paradigm, moves computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. This crucial shift from centralized data centers to edge devices, such as smartphones, IoT sensors, and industrial controllers, significantly reduces latency and improves response times for applications requiring real-time processing. This decentralized approach allows for faster processing of data, which is especially vital for applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and real-time video streaming where immediate reactions are paramount. This also enables quicker data analysis, leading to faster insights and quicker responses.
The reduced reliance on centralized servers minimizes network congestion and enhances data security. Storing and processing data locally minimizes the risk of data breaches and ensures greater control over sensitive information. Edge devices can perform computations and analysis without transmitting data to remote servers, reducing the bandwidth demands on the network and allowing for greater efficiency in resource utilization. This decentralized architecture also provides a greater resilience to network failures, as localized processing can continue even if the central network experiences disruptions.
Key Benefits of Edge Computing in Real-Time Applications
Edge computing offers a plethora of advantages for real-time applications. One of the most significant benefits is the dramatic reduction in latency. By processing data closer to the source, edge devices can respond to events much more quickly, enabling real-time decision-making and control. This is particularly important for applications requiring immediate responses, such as industrial automation systems, autonomous vehicles, and medical devices.
Another key advantage is enhanced reliability and resilience. With data processing occurring closer to the source, the system is less susceptible to network outages or bandwidth limitations. This ensures consistent performance even in challenging network conditions, guaranteeing continuous operation for critical applications. This is a significant improvement over traditional cloud-based systems, which can be vulnerable to network disruptions.
Furthermore, edge computing enhances security. By processing data locally, the need to transmit sensitive information across vast networks is reduced, minimizing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. This localized processing gives organizations greater control over their data and enhances the security of their systems.
Finally, edge computing can lead to significant cost savings by optimizing resource utilization. By reducing the need for extensive data transfer and processing in centralized data centers, edge computing can help organizations save on infrastructure costs and improve overall efficiency.

Securing Data and Ensuring Privacy in Edge Environments
Data Encryption at the Edge
Protecting sensitive data traversing edge devices and networks is paramount. Robust encryption mechanisms are crucial to safeguard information from unauthorized access, especially in environments where data transmission might occur over less secure connections. Implementing end-to-end encryption protocols, ensuring data is encrypted both at the source and destination, is a best practice. This ensures that even if an intermediary node is compromised, the data remains protected. Advanced encryption standards and key management systems are essential components of a comprehensive security strategy for edge environments.
Choosing the right encryption algorithm for the specific data type and sensitivity level is also critical. Factors like performance implications and compatibility with different edge devices need careful consideration. Implementing regular security audits and penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of the chosen encryption strategies.
Access Control and Authentication
Implementing strict access controls and robust authentication procedures is vital for preventing unauthorized access to edge devices and the data they process. This includes using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control (RBAC) to limit user permissions. Regularly reviewing and updating access control policies is crucial to adapt to evolving security threats and changing organizational needs. This approach minimizes the risk of data breaches and maintains the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
Employing secure protocols for user authentication, such as Secure Shell (SSH) and Transport Layer Security (TLS), is essential to verify the identity of users connecting to edge devices. These protocols establish secure channels for communication, protecting against eavesdropping and tampering.
Data Integrity and Validation
Ensuring data integrity is crucial to maintaining the reliability and accuracy of information processed at the edge. Implementing checksums and hash functions helps detect any unauthorized modifications to data during transmission or storage. This proactive approach helps verify the data's authenticity and prevent malicious manipulation. Maintaining a robust audit trail for data changes allows for efficient troubleshooting and accountability in case of issues or security incidents. This is vital in environments where data integrity is paramount.
Privacy Compliance and Regulations
Adhering to relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is essential for organizations operating in edge environments. Implementing data anonymization techniques and data masking procedures helps protect user privacy while enabling data analysis. Careful consideration of data retention policies is critical to ensure compliance with legal requirements. This involves establishing clear guidelines for data storage duration and securely deleting or archiving data as per regulatory mandates.
Secure Software Development Practices
Adopting secure software development practices throughout the entire lifecycle of edge applications is critical. This includes incorporating security considerations into the design, development, and deployment phases. Employing secure coding practices minimizes vulnerabilities and reduces the risk of exploits. Regular security assessments and penetration testing of edge applications are vital for identifying and addressing potential weaknesses. Implementing vulnerability scanning tools and employing a DevSecOps approach can improve the overall security posture of edge systems. This ensures the software remains secure and resilient against evolving threats.