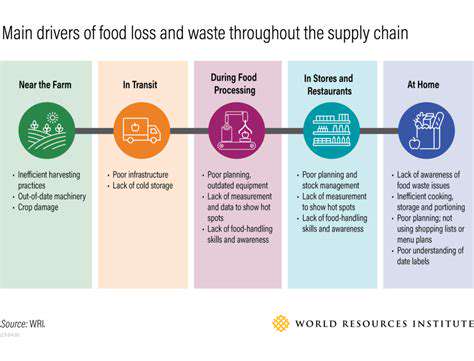
Key Features and Benefits of Smart Contracts
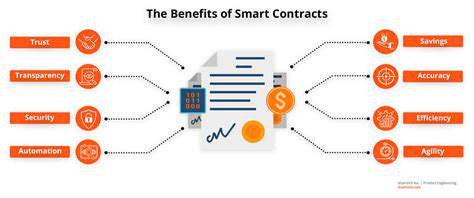
Enhanced Security
Smart home systems offer significantly improved security measures compared to traditional methods. Sophisticated sensors and automated responses can deter intruders and detect unusual activity, providing a strong first line of defense against potential threats. This proactive approach to security goes beyond simple locks and alarms, offering a comprehensive security solution for your home.
Furthermore, many smart home systems allow for remote monitoring and control of security features. This means you can check on your home and activate security systems from anywhere in the world, giving you peace of mind and enhanced security even when you are away. This constant vigilance significantly reduces the risk of break-ins and other security breaches.
Convenience and Efficiency
One of the most appealing aspects of smart home technology is its ability to streamline daily tasks and improve overall convenience. Imagine effortlessly controlling lighting, temperature, and appliances from your smartphone or voice commands. This level of control frees up valuable time and allows you to focus on more important things.
Smart home systems can also help you manage your energy consumption more effectively. Automated adjustments to lighting and heating based on your schedule and environmental conditions can lead to significant energy savings over time. This not only benefits your wallet but also contributes to a more sustainable lifestyle.
Improved Accessibility
Smart home technology can significantly improve the lives of individuals with disabilities. Many smart devices can be customized to address specific needs, providing greater independence and control over the home environment. For example, voice-activated systems can make tasks like turning on lights or adjusting the thermostat much easier and more accessible.
Furthermore, automated systems can provide assistance with everyday tasks, such as opening doors or managing appliances. These features can enhance the safety and independence of individuals with disabilities, enabling them to live more comfortably and autonomously in their homes. This feature is crucial for improving overall quality of life for many.
Cost Savings and Sustainability
Smart home systems can offer significant long-term cost savings through energy efficiency. By optimizing energy consumption and reducing waste, these systems can reduce your monthly utility bills, saving you money over the long run. Smart thermostats can learn your preferences and automatically adjust the temperature to save energy, leading to substantial savings on your heating and cooling bills.
Moreover, many smart home features promote a more sustainable lifestyle by reducing energy consumption and water usage. This contributes to a smaller environmental footprint and helps protect the planet for future generations. These features contribute to a greener and more sustainable way to live at home.
Customization and Personalization
Smart home systems offer a high degree of customization and personalization, allowing you to tailor your home environment to your specific needs and preferences. From setting personalized lighting schedules to creating unique security protocols, these features allow you to create a truly unique and comfortable living space. This freedom of customization is a key feature that sets smart home technology apart from traditional systems.
The ability to integrate various smart devices into a unified system gives you complete control over the functionality of your home. You can create personalized routines and automate tasks based on your schedule and preferences, making your home truly responsive to your needs.
Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart Contracts in Supply Chain Management
Smart contracts can revolutionize supply chain management by automating various processes, from tracking goods' movement to verifying product authenticity. Imagine a system where every stage of a product's journey, from raw material sourcing to delivery, is recorded and verified on a blockchain. This transparency and immutability enhance trust among stakeholders, reducing fraud and errors, and improving efficiency across the entire supply chain. Smart contracts can also trigger payments automatically upon the completion of specific milestones, streamlining financial transactions and reducing administrative overhead.
Automating Agricultural Processes
The agricultural sector can benefit significantly from smart contracts in automating tasks like land management, crop insurance, and trading. Smart contracts can automatically transfer land ownership based on pre-defined conditions, ensuring transparency and security in land transactions. They can also automate the payout of crop insurance claims based on predefined parameters, reducing delays and improving the efficiency of the process. Furthermore, smart contracts can facilitate transparent and secure trading of agricultural products, connecting farmers directly with buyers and minimizing the involvement of intermediaries.
Streamlining Real Estate Transactions
Smart contracts hold the potential to transform real estate transactions by automating and streamlining the process. They can automate the transfer of ownership, ensuring that all legal requirements are met and that the transaction is secure and transparent. Smart contracts can also facilitate the payment of property taxes and other related fees, reducing administrative burden and preventing delays. With the ability to automatically trigger actions based on predefined conditions, smart contracts can expedite the entire process, benefiting both buyers and sellers.
Securing Intellectual Property Rights
Smart contracts can play a crucial role in protecting intellectual property rights by providing a secure and transparent platform for managing licenses and royalties. Imagine a system where the rights to use a piece of software or a piece of creative content are automatically managed and verified on a blockchain, ensuring that creators are compensated fairly and promptly. This automated system reduces the risk of infringement and facilitates the tracking of intellectual property usage, adding a layer of security and transparency to the process.
Enhancing Financial Transactions in Agriculture
Smart contracts can dramatically improve financial transactions in the agricultural industry by automating payments, reducing fraud, and improving transparency. They can create a system where payments are automatically triggered upon the delivery of goods or the completion of tasks, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing delays. This automation can also help to mitigate the risk of fraud and improve the efficiency of the entire financial process. Smart contracts can also create new and innovative financial instruments that are tailored to the specific needs of agricultural businesses.
Improving Transparency and Trust in Procurement
Smart contracts have the potential to enhance transparency and trust in procurement processes. By automating the bidding process and ensuring that all requirements are met, smart contracts can help to create a more fair and transparent marketplace. This automated system can also improve accountability, as all transactions are recorded on the blockchain, making it easier to track and audit procurement activities. Smart contracts can verify the authenticity of goods and services, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing trust among suppliers and buyers.
Facilitating Microfinance and Crowdfunding
Smart contracts can enable innovative approaches to microfinance and crowdfunding initiatives, creating new opportunities for individuals and small businesses in underserved communities. They can automate the disbursement of funds based on predefined conditions, ensuring that loans are repaid and that funds are disbursed to deserving recipients. This automation can significantly reduce administrative overhead and improve access to capital for individuals and small businesses. Furthermore, smart contracts can facilitate peer-to-peer lending platforms, connecting individuals and businesses with affordable financing options.
Challenges and Considerations for Smart Contract Development

Implementing Effective Data Governance
Implementing effective data governance requires a multifaceted approach that considers various factors, including the organization's specific needs, resources, and existing infrastructure. A robust data governance framework must establish clear roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing data throughout its lifecycle, from collection to disposal. This includes defining data quality standards, establishing data security protocols, and implementing procedures for data access and usage. Failing to address these critical aspects can lead to data silos, inconsistencies, and compliance issues.
Data governance is not a one-time project; it's an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation. Regular audits and assessments are essential to ensure that the implemented policies and procedures remain effective and aligned with the organization's evolving needs. This also involves training and educating personnel on data governance principles and best practices, fostering a culture of data awareness and responsibility within the organization.
Addressing Data Silos and Inconsistency
Data silos, where data is scattered across different departments or systems without a centralized view, create significant challenges for data governance. This fragmentation often leads to data inconsistencies, making it difficult to derive accurate insights and make informed decisions. Effective data governance strategies need to break down these silos by establishing standardized data models, dictionaries, and definitions. This standardization promotes data consistency and interoperability, enabling the integration of data from different sources for more comprehensive analysis.
A critical aspect of addressing data silos is implementing a data catalog that provides a comprehensive inventory of all data assets within the organization. This catalog facilitates data discovery and reuse, reducing the risk of data duplication and promoting data sharing across departments. It also helps to identify potential data quality issues and inconsistencies early on, enabling proactive remediation.
Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Data security is paramount in any data governance strategy. Robust security measures are crucial to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This includes implementing access controls, encryption, and regular security audits. Failure to implement strong security measures can result in significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Compliance with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is another critical consideration. Organizations need to ensure their data governance practices align with these regulations, potentially requiring specific policies and procedures to be in place. This necessitates a thorough understanding of the regulations and their implications for the organization's data management practices. This also necessitates careful consideration of the implications of these regulations for the organization's data management practices.
Managing Data Quality and Integrity
Maintaining data quality and integrity is essential for ensuring reliable and trustworthy data. This involves establishing clear data quality standards, implementing data validation rules, and establishing processes for data cleansing and correction. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate analysis, flawed decision-making, and ultimately, a negative impact on business operations. Implementing data quality checks at each stage of the data lifecycle can significantly reduce the likelihood of errors and inconsistencies.
Regular monitoring and auditing of data quality are crucial for identifying and addressing issues promptly. This involves tracking key data quality metrics, analyzing data trends, and implementing corrective actions as needed. This proactive approach ensures data accuracy and reliability, thereby supporting informed decision-making and improved business outcomes.