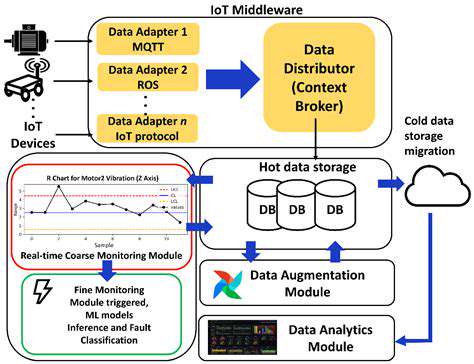
Beyond Key Distribution: Exploring Applications

Beyond the Basics of Key Exchange
Traditional key distribution methods struggle with modern security challenges. The exponential growth in required keys creates logistical nightmares, while compromised communication channels jeopardize entire security architectures. These limitations demand more sophisticated approaches than basic key exchange protocols can provide.
Quantum Cryptography: A Paradigm Shift
Quantum techniques fundamentally transform key distribution by leveraging nature's laws rather than mathematical complexity. Quantum keys remain secure because measurement attempts unavoidably alter their state, creating a perfect tamper-detection system. This physics-based security represents a monumental leap forward for cryptographic systems.
Post-Quantum Cryptography: Preparing for the Future
The quantum computing revolution necessitates cryptographic algorithms resistant to quantum attacks. Developing and standardizing post-quantum cryptography has become an urgent global priority, requiring substantial infrastructure updates to protect sensitive data against future threats.
The Role of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain's decentralized architecture offers promising solutions for secure key management. Distributed ledgers provide tamper-proof key storage, reducing reliance on vulnerable centralized systems while enhancing resilience against attacks.
Advanced Key Management Systems
Modern systems now integrate comprehensive key lifecycle management, from generation to revocation. Automated controls and robust access management streamline operations while significantly improving security posture across complex digital environments.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Identity Management
These cryptographic techniques enable verification without disclosure of sensitive information. Zero-knowledge proofs revolutionize identity validation, allowing authentication while preserving privacy - crucial for secure digital interactions.
Security Audits and Continuous Improvement
Ongoing assessment and proactive vulnerability management form the backbone of effective security. Regular audits and system updates ensure resilience against evolving threats in our rapidly changing digital landscape.
Challenges and Future Directions
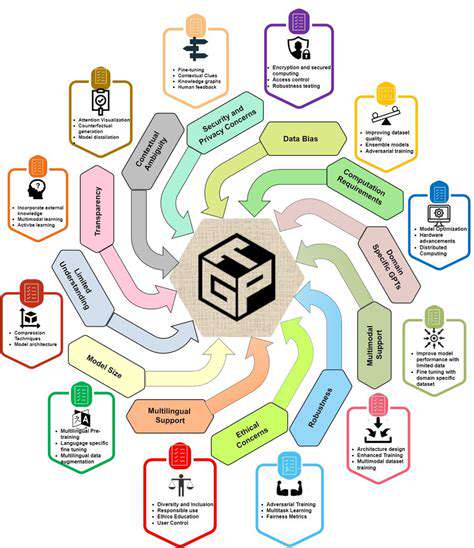
Overcoming Data Silos
Organizational data fragmentation creates significant analytical challenges. Breaking down these silos requires coordinated data standardization efforts to enable comprehensive business insights and informed decision-making.
Addressing Data Quality Issues
Reliable analytics demand rigorous data validation procedures to eliminate inaccuracies and inconsistencies. This quality assurance process represents a foundational requirement for any data-driven strategy.
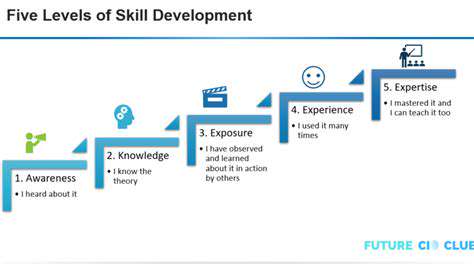
Evolving Data Skills and Expertise
The data revolution necessitates workforce upskilling. Investing in data literacy programs has become essential for organizations seeking to harness their information assets effectively.
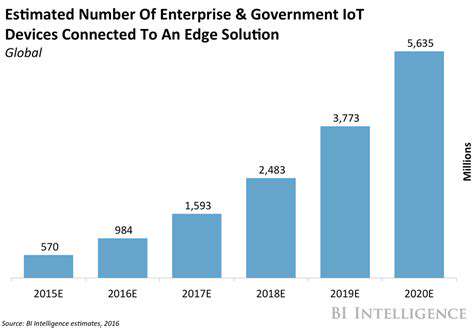
Scalability and Infrastructure
Expanding data volumes require robust, scalable architectures capable of processing information efficiently. Proper infrastructure planning prevents performance bottlenecks in analytics workflows.
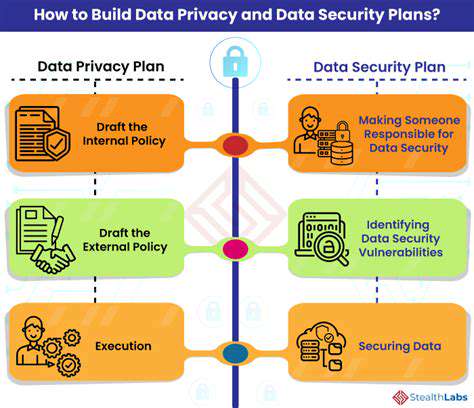
Maintaining Data Security and Privacy
Protecting sensitive information requires comprehensive security measures aligned with evolving regulations. Data encryption and access controls form critical components of modern security frameworks.
Ethical Considerations in Data Usage
Responsible data practices must address potential biases and privacy concerns. Developing ethical guidelines ensures fair, transparent use of data analytics across all applications.