Introduction to Edge AI in Agriculture
Understanding Edge AI
Edge AI, in the context of agriculture, refers to the deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) processing power directly at the source of data generation, like on a farm or within a greenhouse. Instead of sending all the data to a centralized cloud server for processing, edge AI devices analyze the data locally. This approach offers significant advantages, particularly in scenarios with limited or unreliable internet connectivity, where the latency associated with cloud-based processing would be detrimental. Edge AI solutions offer real-time analysis and decision-making capabilities, which are crucial for optimizing agricultural processes and responding quickly to emerging issues.
A key aspect of edge AI is the use of specialized hardware and software tailored for efficient data processing. This includes powerful microprocessors, specialized AI chips, and algorithms optimized for specific agricultural tasks. These components are crucial in enabling quick and accurate analysis, ensuring that the insights gained from the data are actionable and not delayed.
Benefits of Edge AI in Agriculture
Implementing edge AI in agriculture presents a wealth of benefits. One primary advantage is enhanced efficiency in various agricultural processes. Real-time data analysis allows for swift adjustments in irrigation, fertilization, or pest control strategies, minimizing resource waste and maximizing yield. This also contributes to a more sustainable agricultural practice by reducing the environmental impact of these operations.
Another significant benefit is the improved responsiveness to critical events. For example, detecting crop diseases early on through image analysis can be crucial to prevent widespread infestations and implement targeted interventions. Edge AI's ability to act quickly on this information translates to minimized crop damage and increased overall profitability. This rapid response is especially vital in situations involving rapidly evolving problems.
Furthermore, edge AI solutions can greatly enhance data security and privacy. By processing data locally, there is reduced risk of data breaches or exposure to unauthorized access, which is paramount in the context of sensitive agricultural information.
Edge AI for Crop Disease Detection
One of the most promising applications of edge AI in agriculture is the early detection of crop diseases. Sophisticated image recognition algorithms, running on edge devices, can analyze images captured by drones or cameras to identify subtle signs of disease, potentially at a much earlier stage than traditional methods. This early detection allows for quicker implementation of targeted treatments, preventing widespread disease outbreaks and maximizing crop yields.
Edge AI can also analyze environmental data, such as temperature, humidity, and soil conditions, to predict the likelihood of disease development. Combining these factors with visual analysis further strengthens the accuracy of disease prediction models. This proactive approach is a significant step forward in preventative agriculture.
Challenges and Future Directions
While edge AI offers exciting possibilities for smart agriculture, challenges remain. Developing robust and accurate AI models for various crop types and disease identification is a significant hurdle. Furthermore, the cost of implementing and maintaining edge AI infrastructure needs careful consideration. However, advancements in AI chip technology and decreasing hardware costs are steadily mitigating these challenges.
Future research in edge AI for agriculture will likely focus on developing more sophisticated models for complex disease identification and integrating multiple data sources, including weather patterns, soil conditions, and even historical data. This comprehensive approach will enable more precise predictions and proactive strategies for optimal crop health and yield.
The Role of Image Recognition in Disease Identification
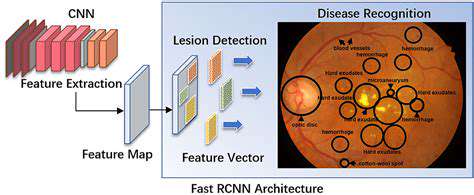
Image Recognition in Data Analysis
Image recognition, a crucial component of artificial intelligence, plays a transformative role in data analysis. Its ability to identify and categorize objects, patterns, and features within images empowers businesses and researchers to extract valuable insights from vast datasets, leading to more informed decisions and improved outcomes. From medical imaging to satellite imagery, the applications are diverse and impactful. Image recognition algorithms can analyze complex visual data, automating tasks that would otherwise be time-consuming and labor-intensive for human analysts.
The advancement of deep learning techniques has significantly boosted the accuracy and efficiency of image recognition systems. These sophisticated algorithms learn from vast amounts of labeled data, enabling them to identify intricate details and subtle variations that might be missed by traditional methods. This, in turn, allows for more precise and reliable data analysis, leading to better predictions and actionable strategies.
Applications Across Industries
The applications of image recognition extend far beyond academic research. In the healthcare sector, image recognition is revolutionizing diagnostics, enabling quicker and more accurate identification of diseases like cancer from medical scans. Furthermore, in agriculture, image recognition is used to monitor crop health, detect pests, and optimize irrigation strategies, resulting in increased yields and reduced resource consumption.
Beyond these specific examples, image recognition is also used in various sectors like automotive, security, and retail. Automated systems can identify objects, faces, and even emotions, leading to improvements in safety, security, and customer experience. For instance, self-driving cars rely heavily on image recognition to perceive their surroundings, making decisions that lead to safer navigation. The rapid development of these systems is creating a significant impact on different industries.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its numerous benefits, image recognition faces some challenges. Data quality and quantity are crucial factors affecting the accuracy and reliability of the results. Ensuring that the training data is representative and free of biases is essential for avoiding flawed or discriminatory outcomes. Also, the computational resources required for training and deploying complex image recognition models can be substantial, posing a barrier for some organizations.
Looking ahead, ongoing research focuses on improving the robustness and adaptability of image recognition models to various lighting conditions, image resolutions, and different object orientations. Further advancements in deep learning and related technologies will likely lead to even more sophisticated image recognition systems, capable of handling more complex and challenging scenarios. This will, in turn, open up new avenues for innovation and create even more possibilities for its use in various fields.
Future Trends and Challenges

Emerging Technologies
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize various industries, presenting both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. AI-powered automation is set to reshape the workforce, potentially leading to job displacement in certain sectors. However, it also promises to create new roles and opportunities in areas like AI development and maintenance.
Similarly, the increasing adoption of blockchain technology is transforming how we manage data and transactions, offering enhanced security and transparency. This technology holds immense potential for streamlining supply chains and fostering trust in digital interactions, but navigating the complexities of its implementation and regulation is crucial.
Sustainable Practices
Environmental consciousness is driving a global shift towards sustainable practices. Companies are increasingly prioritizing environmentally friendly operations, reducing their carbon footprint, and adopting circular economy models. This trend is impacting supply chains, manufacturing processes, and product design, encouraging the development of eco-friendly alternatives and resource efficiency.
Data Privacy and Security
The rise of digital technologies has led to an unprecedented volume of data being collected and processed. Protecting this data from breaches and misuse is paramount. The need for robust data privacy regulations and secure data management systems is becoming increasingly critical, especially in light of the growing sophistication of cyber threats.
Individuals and organizations must be more vigilant about protecting sensitive information and adhering to privacy guidelines. Stricter enforcement of data protection laws will be essential to maintain trust in digital systems.
Globalization and Interconnectedness
Globalization continues to shrink the world, fostering greater interconnectedness and collaboration across borders. This interconnectedness creates new avenues for trade, investment, and cultural exchange, but also presents challenges related to communication, coordination, and managing diverse interests.
International collaborations and agreements are essential for addressing global issues like climate change, pandemics, and economic instability. Building strong relationships and fostering mutual understanding are vital for navigating the complexities of an increasingly interconnected world.
Skills Gap and Workforce Development
The changing nature of work demands a workforce equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge. This is creating a skills gap in many industries, as traditional jobs are automated, and new roles emerge requiring specialized expertise. Investing in education and training programs is crucial to bridge this gap and ensure that individuals can adapt to the evolving job market.
Economic Inequality and Social Justice
The benefits of technological advancements and globalization are not always distributed equitably. Addressing economic inequality and fostering social justice are critical to ensuring that the progress of society is inclusive and benefits all members of society. Policies that promote fair wages, access to education, and social mobility are essential to create a more just and equitable world.
Addressing systemic issues like discrimination and lack of opportunity can help ensure that the benefits of economic growth are shared more broadly. This requires a multi-faceted approach that tackles the root causes of inequality and promotes inclusivity.
Ethical Considerations in Technology
As technology continues to evolve, we must carefully consider its ethical implications. Questions surrounding artificial intelligence, genetic engineering, and other emerging technologies demand thoughtful consideration and ethical frameworks. Establishing responsible guidelines and regulations is vital to ensure that advancements are used for the benefit of humanity and not for malicious purposes.
Transparency, accountability, and inclusivity must be central to the development and deployment of new technologies. Open discussions, public consultations, and the involvement of diverse perspectives are necessary to navigate the ethical challenges that lie ahead.